Technique Innovation and Clinical Application of Electrical Impedance Tomography: Bibliometric Research from 2001 to 2020
- PMID: 35581904
- PMCID: PMC9126035
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.936327
Technique Innovation and Clinical Application of Electrical Impedance Tomography: Bibliometric Research from 2001 to 2020
Abstract
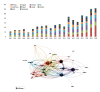
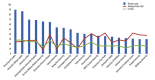
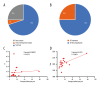
BACKGROUND Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a new test that has been widely used by clinicians in recent years at bedside or in ICU wards. Studies and publications on EIT increased quickly and the hotspot trends changed; however, the overview and characteristics of such studies have not yet been reported. Therefore, we have attempted to interpret the evolution of EIT and to anticipate its possible future clinical use by conducting a statistical analysis of EIT articles over the past 20 years. MATERIAL AND METHODS We analyzed EIT-related articles from 2020 and the 20 years prior, sourced from the Web of Science database. The data collected included the number of articles published, the classification of the articles, basic information, and author affiliation. RESULTS Our study retrieved a total of 1427 EIT-related articles through screening, with the most articles published from Chinese authors and the Chinese Air Force Military Medical University, and the most cited article type being EIT-related basic research. Most articles on EIT have been published in the journal Physiological Measurement. Furthermore, the hotspots and research trends of EIT have changed from basic innovation development to clinical application in the past 20 years. CONCLUSIONS This paper presents a statistical analysis of articles on EIT over the last 20 years, focusing on trends from the mechanisms of EIT to its clinical use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Research Trends and Hotspots of Medical Electrical Impedance Tomography Algorithms: A Bibliometric Analysis From 1987 to 2021.Cureus. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):e49700. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49700. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging trends and hot spots on electrical impedance tomography extrapulmonary applications.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 21;8(12):e12458. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12458. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36619470 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and hotspots in the field of electrical impedance tomography for mechanical ventilation: a bibliometric analysis.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Mar 29;16(3):2070-2081. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-98. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38617762 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Trends and Hot Spots of Electrical Impedance Tomography Applications in Clinical Lung Monitoring.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 31;8:813640. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.813640. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35174185 Free PMC article.
-
The 100 most-cited original articles in cardiac computed tomography: A bibliometric analysis.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2016 Sep-Oct;10(5):414-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2016.07.013. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2016. PMID: 27452312 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Trends and Hotspots of Medical Electrical Impedance Tomography Algorithms: A Bibliometric Analysis From 1987 to 2021.Cureus. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):e49700. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49700. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging trends and hot spots on electrical impedance tomography extrapulmonary applications.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 21;8(12):e12458. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12458. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36619470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler A, Amyot R, Guardo R, et al. Monitoring changes in lung air and liquid volumes with electrical impedance tomography. J Appl Physiol. 1997;83(5):1762–67. - PubMed
-
- Adler A, Shinozuka N, Berthiaume Y, et al. Electrical impedance tomography can monitor dynamic hyperinflation in dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1998;84(2):726–32. - PubMed
-
- Barber DC, Brown BH. Applied potential tomography. J Phys E. 1984;17(9):723–33.
-
- Brown BH, Barber DC, Seagar AD. Applied potential tomography – possible clinical-applications. Clin Phys Physiol Meas. 1985;6(2):109–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

