Oxidative stress and redox signaling in CRPC progression: therapeutic potential of clinically-tested Nrf2-activators
- PMID: 35582006
- PMCID: PMC9019181
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2020.71
Oxidative stress and redox signaling in CRPC progression: therapeutic potential of clinically-tested Nrf2-activators
Abstract
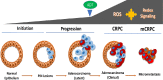
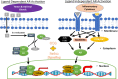
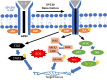
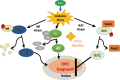
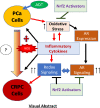
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is the mainstay regimen in patients with androgen-dependent prostate cancer (PCa). However, the selection of androgen-independent cancer cells leads to castrate resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). The aggressive phenotype of CRPC cells underscores the need to elucidate mechanisms and therapeutic strategies to suppress CRPC outgrowth. Despite ADT, the activation of androgen receptor (AR) transcription factor continues via crosstalk with parallel signaling pathways. Understanding of how these signaling cascades are initiated and amplified post-ADT is lacking. Hormone deprivation can increase oxidative stress and the resultant reactive oxygen species (ROS) may activate both AR and non-AR signaling. Moreover, ROS-induced inflammatory cytokines may further amplify these redox signaling pathways to augment AR function. However, clinical trials using ROS quenching small molecule antioxidants have not suppressed CRPC progression, suggesting that more potent and persistent suppression of redox signaling in CRPC cells will be needed. The transcription factor Nrf2 increases the expression of numerous antioxidant enzymes and downregulates the function of inflammatory transcription factors, e.g., nuclear factor kappa B. We documented that Nrf2 overexpression can suppress AR-mediated transcription in CRPC cell lines. Furthermore, two Nrf2 activating agents, sulforaphane (a phytochemical) and bardoxolone-methyl (a drug in clinical trial) suppress AR levels and sensitize CRPC cells to anti-androgens. These observations implicate the benefits of potent Nrf2-activators to suppress the lethal signaling cascades that lead to CRPC outgrowth. This review article will address the redox signaling networks that augment AR signaling during PCa progression to CRPC, and the possible utility of Nrf2-activating agents as an adjunct to ADT.
Keywords: Nrf2; Nrf2-activators; Prostate cancer; androgen receptor; endocrine resistance; hormone therapy; oxidative stress; redox signaling.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
