Perspectives of nano-carrier drug delivery systems to overcome cancer drug resistance in the clinics
- PMID: 35582007
- PMCID: PMC9019183
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2020.59
Perspectives of nano-carrier drug delivery systems to overcome cancer drug resistance in the clinics
Abstract
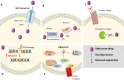
Advanced cancer is still considered an incurable disease because of its metastatic spread to distal organs and progressive gain of chemoresistance. Even though considerable treatment progress and more effective therapies have been achieved over the past years, recurrence in the long-term and undesired side effects are still the main drawbacks of current clinical protocols. Moreover, a majority of chemotherapeutic drugs are highly hydrophobic and need to be diluted in organic solvents, which cause high toxicity, in order to reach effective therapeutic dose. These limitations of conventional cancer therapies prompted the use of nanomedicine, the medical application of nanotechnology, to provide more effective and safer cancer treatment. Potential of nanomedicines to overcome resistance, ameliorate solubility, improve pharmacological profile, and reduce adverse effects of chemotherapeutical drugs is thus highly regarded. Their use in the clinical setting has increased over the last decade. Among the various existing nanosystems, nanoparticles have the ability to transform conventional medicine by reducing the adverse effects and providing a controlled release of therapeutic agents. Also, their small size facilitates the intracellular uptake. Here, we provide a closer review of clinical prospects and mechanisms of action of nanomedicines to overcome drug resistance. The significance of specific targeting towards cancer cells is debated as well.
Keywords: Drug delivery systems; cancer treatment; nanomedicine; resistance.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Novel nanomedicines to overcome cancer multidrug resistance.Drug Resist Updat. 2021 Sep;58:100777. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2021.100777. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Drug Resist Updat. 2021. PMID: 34481195 Review.
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
A review of the current scientific and regulatory status of nanomedicines and the challenges ahead.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2011 Mar-Apr;65(2):177-95. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2011. PMID: 21502077 Review.
-
Surface-Engineered Cancer Nanomedicine: Rational Design and Recent Progress.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(11):1181-1190. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200214110645. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32056517 Review.
-
Targeting cancer cells with nanotherapeutics and nanodiagnostics: Current status and future perspectives.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Feb;69:52-68. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.01.011. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 32014609 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive peptides from food science to pharmaceutical industries: Their mechanism of action, potential role in cancer treatment and available resources.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 22;10(23):e40563. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40563. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39654719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine and versatile therapies for cancer treatment.MedComm (2020). 2022 Aug 18;3(3):e163. doi: 10.1002/mco2.163. eCollection 2022 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35992969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Microfluidic Approach for Intracellular Delivery into Red Blood Cells: A Deeper Understanding of the Role of Chemical/Rheological Properties of the Cellular Suspension.Ann Biomed Eng. 2025 May;53(5):1128-1137. doi: 10.1007/s10439-025-03678-2. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Ann Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 39971860 Free PMC article.
-
Lonicerae Japonicae Flos with the homology of medicine and food: a review of active ingredients, anticancer mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, quality control, toxicity and applications.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 9;14:1446328. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1446328. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39314630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Cancer and Anti-Oxidant Effects of Fenoferin-loaded Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticles Coated with Folic Acid-bound Chitosan.Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(5):614-625. doi: 10.2174/0115665240283529240202095254. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 38375838
References
-
- The Global Cancer Observatory, Europe Globocan 2018, (2020) 1-2. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/908-europe-fact-sh... [Last accessed on 19 Nov 2020]
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
