A Cross-Disciplinary View of Testing and Bioinformatic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Human Respiratory Viruses in Pandemic Settings
- PMID: 35582017
- PMCID: PMC8843158
- DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3133417
A Cross-Disciplinary View of Testing and Bioinformatic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Human Respiratory Viruses in Pandemic Settings
Abstract
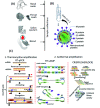
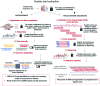
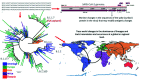
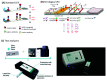
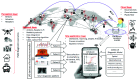
The SARS-Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infectious disease, COVID-19, has spread rapidly, resulting in a global pandemic with significant mortality. The combination of early diagnosis via rapid screening, contact tracing, social distancing and quarantine has helped to control the pandemic. The absence of real time response and diagnosis is a crucial technology shortfall and is a key reason why current contact tracing methods are inadequate to control spread. In contrast, current information technology combined with a new generation of near-real time tests offers consumer-engaged smartphone-based "lab-in-a-phone" internet-of-things (IoT) connected devices that provide increased pandemic monitoring. This review brings together key aspects required to create an entire global diagnostic ecosystem. Cross-disciplinary understanding and integration of both mechanisms and technologies for effective detection, incidence mapping and disease containment in near real-time is summarized. Available measures to monitor and/or sterilize surfaces, next-generation laboratory and smartphone-based diagnostic approaches can be brought together and networked for instant global monitoring that informs Public Health policy. Cloud-based analysis enabling real-time mapping will enable future pandemic control, drive the suppression and elimination of disease spread, saving millions of lives globally. A new paradigm is introduced - scaled and multiple diagnostics for mapping and spreading of a pandemic rather than traditional accumulation of individual measurements. This can do away with the need for ultra-precise and ultra-accurate analysis by taking mass measurements that can relax tolerances and build resilience through networked analytics and informatics, the basis for novel swarm diagnostics. These include addressing ethical standards, local, national and international collaborative engagement, multidisciplinary and analytical measurements and standards, and data handling and storage protocols.
Keywords: Antibody test; COVID-19; Internet-of-Things; LAMP test; PCR; SARS-CoV; antigen test; bioinformatics; lab-in-a-phone; point-of-care test.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of four different strategies for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the general population (CoV-Surv Study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a cluster-randomised, two-factorial controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 8;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04982-z. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33419461 Free PMC article.
-
Internet of things (IoT) imbedded point-of-care SARS-CoV-2 testing in the pandemic and post-pandemic era.Biosaf Health. 2022 Dec;4(6):365-368. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2022.09.005. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Biosaf Health. 2022. PMID: 36168401 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-tiered screening and diagnosis strategy for COVID-19: a model for sustainable testing capacity in response to pandemic.Ann Med. 2020 Aug;52(5):207-214. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1763449. Epub 2020 May 14. Ann Med. 2020. PMID: 32370561 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 what have we learned? The rise of social machines and connected devices in pandemic management following the concepts of predictive, preventive and personalized medicine.EPMA J. 2020 Jul 30;11(3):311-332. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00218-x. eCollection 2020 Sep. EPMA J. 2020. PMID: 32839666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 Sensing at Point-of-Care and Artificial Intelligence for Intelligent COVID-19 Management.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020 Nov 16;3(11):7306-7325. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01004. Epub 2020 Oct 27. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020. PMID: 35019473 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a bionic IoT: Environmental monitoring using smartphone interrogated plant sensors.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 10;18(2):e0265856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265856. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36763639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Accessed: Nov. 30, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Verdoni L., Mazza A., Gervasoni A., Martelli L., Ruggeri M., Ciuffreda M., Bonanomi E., and D’Antiga L., “An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study,” Lancet, vol. 395, no. 10239, pp. 1771–1778, Jun. 2020. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
