Nanocarrier drug resistant tumor interactions: novel approaches to fight drug resistance in cancer
- PMID: 35582024
- PMCID: PMC9019274
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2020.81
Nanocarrier drug resistant tumor interactions: novel approaches to fight drug resistance in cancer
Abstract
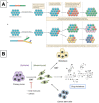
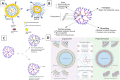
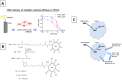
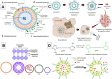
Cancer is one of the biggest healthcare concerns in our century, a disease whose treatment has become even more difficult following reports of drug-resistant tumors. When this happens, chemotherapy treatments fail or decrease in efficiency, leading to catastrophic consequences to the patient. This discovery, along with the fact that drug resistance limits the efficacy of current treatments, has led to a new wave of discovery for new methods of treatment. The use of nanomedicine has been widely studied in current years as a way to effectively fight drug resistance in cancer. Research in the area of cancer nanotechnology over the past decades has led to tremendous advancement in the synthesis of tailored nanoparticles with targeting ligands that can successfully attach to chemotherapy-resistant cancer by preferentially accumulating within the tumor region through means of active and passive targeting. Consequently, these approaches can reduce the off-target accumulation of their payload and lead to reduced cytotoxicity and better targeting. This review explores some categories of nanocarriers that have been used in the treatment of drug-resistant cancers, including polymeric, viral, lipid-based, metal-based, carbon-based, and magnetic nanocarriers, opening the door for an exciting field of discovery that holds tremendous promise in the treatment of these tumors.
Keywords: Drug-resistance; cancer; drug delivery; nanocarriers; nanotechnology.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
