Deep Learning-Based COVID-19 Detection Using CT and X-Ray Images: Current Analytics and Comparisons
- PMID: 35582037
- PMCID: PMC8864950
- DOI: 10.1109/MITP.2020.3036820
Deep Learning-Based COVID-19 Detection Using CT and X-Ray Images: Current Analytics and Comparisons
Abstract
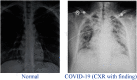
Currently, the world faces a novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) challenge and infected cases are increasing exponentially. COVID-19 is a disease that has been reported by the WHO in March 2020, caused by a virus called the SARS-CoV-2. As of 10 March 2021, more than 150 million people were infected and 3v million died. Researchers strive to find out about the virus and recommend effective actions. An unprecedented increase in pathogens is happening and a major attempt is being made to tackle the epidemic. This article presents deep learning-based COVID-19 detection using CT and X-ray images and data analytics on its spread worldwide. This article's research structure builds on a recent analysis of the COVID-19 data and prospective research to systematize current resources, help the researchers, practitioners by using in-depth learning methodologies to build solutions for the COVID-19 pandemic.
Figures
References
-
- (WHO), W. H. O. Accessed: 18/04/2020. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
-
- Worldometer. Accessed: 10/05/2021. COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. [Online]. Available: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?
-
- Business Insider. Accessed: 18/04/2020. Coronavirus-cases-maps-us-world-spread-symptoms-death-rate-2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.businessinsider.com/coronavirus-cases-maps-us-world-spread-s...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous