Liquid biopsy in metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 35582275
- PMCID: PMC9019210
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2019.84
Liquid biopsy in metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
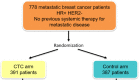
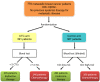
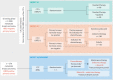
The spread of single tumor cells shed by the primary tumor has been observed in most solid carcinomas and is generally associated with poor clinical outcome. Tumor cells detected in the peripheral blood are commonly referred to as circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and are seen as possible precursors of metastatic disease. Beyond CTCs, circulating tumor DNA and non-coding RNA are increasingly the focus of translation cancer research. In metastatic breast cancer (MBC), elevated levels of CTCs have been confirmed as an independent prognostic factor. While detection of elevated counts after the start of systemic therapy predicts poor response, it is unclear which treatment strategy should be offered in the case of CTC persistence. Currently, the main potentials of blood-based diagnostics in BC are therapy monitoring and liquid biopsy-based treatment interventions. Recently, the first positive study on CTC-guided therapy choices in hormone receptor positive HER2 negative MBC was published. In the present review, we discuss the current data and potential clinical application of liquid biopsy in the metastatic setting.
Keywords: Tumor cell dissemination; breast cancer; circulating tumor DNA; circulating tumor cell; liquid biopsy.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Banys-Paluchowski M received lecture honoraria and served in advisory role for Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, and Eli Lilly. Paluchowski P declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquid Biopsy in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Current Role of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA.Oncol Res Treat. 2022;45(1-2):4-11. doi: 10.1159/000520561. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Oncol Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 34718243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of HER2 phenotype of circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer: a retrospective study in 107 patients.BMC Cancer. 2015 May 14;15:403. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1423-6. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25972110 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of the combined analysis of circulating tumor cells and anti-tumor T-cell immunity in metastatic breast cancer patients.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 23;12:983887. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.983887. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36081561 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating and Disseminated Tumor Cells in Breast Carcinoma: Report from the Consensus Conference on Tumor Cell Dissemination during the 39th Annual Meeting of the German Society of Senology, Berlin, 27 June 2019.Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2019 Dec;79(12):1320-1327. doi: 10.1055/a-1031-1120. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2019. PMID: 31875861 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Mar 30;10(4):192. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10040192. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32235479 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A bibliometric analysis of metastatic breast cancer: two-decade report (2002-2022).Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 24;13:1229222. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1229222. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37692861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashworth TR. A case of cancer in which cells similar to those in tumors were seen in the blood after death. Aus Med J. 1869;14:146–9.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
