Adjuvant Therapy System of COVID-19 Patient: Integrating Warning, Therapy, Post-Therapy Psychological Intervention
- PMID: 35582327
- PMCID: PMC8905612
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3077280
Adjuvant Therapy System of COVID-19 Patient: Integrating Warning, Therapy, Post-Therapy Psychological Intervention
Abstract
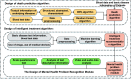
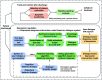
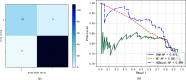
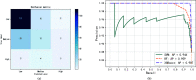
The 2019 novel coronavirus(COVID-19) spreads rapidly, and the large-scale infection leads to the lack of medical resources. For the purpose of providing more reasonable medical service to COVID-19 patients, we designed an novel adjuvant therapy system integrating warning, therapy, and post-therapy psychological intervention. The system combines data analysis, communication networks and artificial intelligence(AI) to design a guidance framework for the treatment of COVID-19 patients. Specifically, in this system, we first can use blood characteristic data to help make a definite diagnosis and classify the patients. Then, the classification results, together with the blood characteristics and underlying diseases disease characteristics of the patient, can be used to assist the doctor in treat treating the patient according to AI algorithms. Moreover, after the patient is discharged from the hospital, the system can monitor the psychological and physiological state at the data collection layer. And in the data feedback layer, this system can analyze the data and report the abnormalities of the patient to the doctor through communication network. Experiments show the effectiveness of our proposed system.
Keywords: 5G communication; COVID-19; adjuvant therapy system; blood characteristic.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence Systems for Diagnosis and Clinical Classification of COVID-19.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 27;12:729455. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.729455. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34650534 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted System in Postoperative Follow-up of Orthopedic Patients: Exploratory Quantitative and Qualitative Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 May 26;22(5):e16896. doi: 10.2196/16896. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32452807 Free PMC article.
-
Emotions of COVID-19: Content Analysis of Self-Reported Information Using Artificial Intelligence.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Apr 30;23(4):e27341. doi: 10.2196/27341. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33819167 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Artificial Intelligence to Address Issues Related to the COVID-19 Virus.SLAS Technol. 2021 Apr;26(2):123-126. doi: 10.1177/2472630320983813. Epub 2021 Jan 4. SLAS Technol. 2021. PMID: 33390088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Imaging-based AI Research - A Literature Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2022;18(5):496-508. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210902103729. Curr Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34473619 Review.
Cited by
-
Sustainable sentiment analysis on E-commerce platforms using a weighted parallel hybrid deep learning approach for smart cities applications.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 3;14(1):26508. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78318-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39489784 Free PMC article.
-
BERT ensemble based MBR framework for android malware detection.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 23;15(1):14027. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98596-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40269058 Free PMC article.
-
DGHSA: derivative graph-based hypergraph structure attack.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 4;14(1):30222. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79824-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39632934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chirico F., Nucera G., and Magnavita N., “Protecting the mental health of healthcare workers during the covid-19 emergency,” BJPsych Int., vol. 18, no. 1, 2021, doi: 10.1192/bji.2020.39. - DOI
-
- Wu J., et al. , “Early antiviral treatment contributes to alleviate the severity and improve the prognosis of patients with novel coronavirus disease (covid-19),” J. Intern. Med., vol. 288, no. 1, pp. 128–138, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Cohen A. N. and Kessel B., “False positives in reverse transcription pcr testing for sars-cov-2,” medRxiv, 2020, doi: 10.1101/2020.04.26.20080911. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
