MYC inhibitors in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 35582389
- PMCID: PMC8992455
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2021.55
MYC inhibitors in multiple myeloma
Abstract
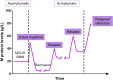
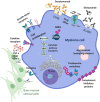
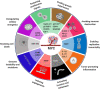
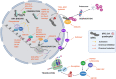
The importance of MYC function in cancer was discovered in the late 1970s when the sequence of the avian retrovirus that causes myelocytic leukemia was identified. Since then, over 40 years of unceasing research have highlighted the significance of this protein in malignant transformation, especially in hematologic diseases. Indeed, some of the earliest connections among the higher expression of proto-oncogenes (such as MYC), genetic rearrangements and their relation to cancer development were made in Burkitt lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukemia and mouse plasmacytomas. Multiple myeloma (MM), in particular, is a plasma cell malignancy strictly associated with MYC deregulation, suggesting that therapeutic strategies against it would be beneficial in treating this disease. However, targeting MYC was - and, somehow, still is - challenging due to its unique properties: lack of defined three-dimensional structure, nuclear localization and absence of a targetable enzymatic pocket. Despite these difficulties, however, many studies have shown the potential therapeutic impact of direct or indirect MYC inhibition. Different molecules have been tested, in fact, in the context of MM. In this review, we summarize the current status of the different compounds, including the results of their clinical testing, and propose to continue with the efforts to identify, repurpose, redesign or improve drug candidates to combine them with standard of care therapies to overcome resistance and enable better management of myeloma treatment.
Keywords: MYC downregulation; MYC inhibition; epigenetics; multiple myeloma; targeted therapies; transcription factor; undruggable target.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Soucek L is founder and shareholder of Peptomyc S.L. and inventor of patent application WO2014180889 A8 that covers the use of the Omomyc mini-protein in medicine, held by VHIO and licensed to Peptomyc. Martínez-Martín S declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GLOBOCAN. Cancer Today. Estimated number of new cases in 2020, WHO Europe (EURO), both sexes, all ages. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-table?v=2020&mode=cancer&mode_... . [Last accessed on 19 Aug 2021]
-
- GLOBOCAN. Cancer Today. Estimated number of new cases in 2020, worldwide, both sexes, all ages. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-table?v=2020&mode=cancer&mode_... . [Last accessed on 19 Aug 2021]
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
