N-acetylcysteine Ameliorates Vancomycin-induced Nephrotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in the in vivo and in vitro Models
- PMID: 35582415
- PMCID: PMC9108398
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.69807
N-acetylcysteine Ameliorates Vancomycin-induced Nephrotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in the in vivo and in vitro Models
Abstract
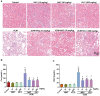
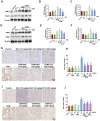
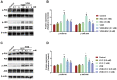
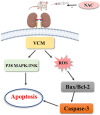
Background: Oxidative stress-related apoptosis is considered as the key mechanism implicated in the pathophysiology of nephrotoxicity with vancomycin (VCM) therapy. We evaluated the possible effects of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on VCM-induced nephrotoxicity and the underlying mechanism. Methods: VCM-induced nephrotoxicity was established using HK-2 cells and SD rats and observed by measuring cell survival, kidney histological changes, renal function and kidney injury related markers (KIM-1 and NGAL). Oxidative stress, renal cell apoptosis and the involved signaling pathways were also evaluated. Results: In model rats, NAC could protect against VCM-induced acute kidney injury with histological damage, renal dysfunction, and increased Cre and BUN levels. In HK-2 cells, VCM-induced decreased cell viability was restored by NAC. In addition, increased expression of caspase-3, KIM-1 and NGAL suffering from VCM was also reversed by NAC in vivo and in vitro. NAC inhibited ROS production, decreased cell apoptosis by decreasing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 expression in HK-2 cells and regulated oxidative stress indicators in the kidney by decreasing GSH, SOD and CAT activity and increasing MDA levels. Furthermore, NAC could effectively reverse VCM-associated increased P38 MAPK/JNK phosphorylation. Conclusions: The results demonstrated that NAC had a protective effect against nephrotoxicity from VCM by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis via P38 MAPK/JNK.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine; nephrotoxicity; oxidative stress; renal protection; vancomycin.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hesperidin ameliorates vancomycin-induced kidney injury via multipathway modulation: Nrf-2/HO-1, Caspase-3/Bax/Bcl-2, ATF-4, KIM-1 and improved renal tissue function.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Oct;240:117131. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.117131. Epub 2025 Jul 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40623456
-
Reno-protective effect of fenofibrate and febuxostat against vancomycin-induced acute renal injury in rats: Targeting PPARγ/NF-κB/COX-II and AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024 Aug;46(4):509-520. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2024.2373216. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024. PMID: 38918173
-
In vivo evidences suggesting the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: protection by erdosteine.Toxicology. 2005 Nov 15;215(3):227-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.07.009. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Toxicology. 2005. PMID: 16112787
-
Effect of N-acetylcysteine on antimicrobials induced nephrotoxicity: a meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Mar 8;26(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04037-y. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40057704 Free PMC article.
-
Vancomycin-Induced Kidney Injury: Animal Models of Toxicodynamics, Mechanisms of Injury, Human Translation, and Potential Strategies for Prevention.Pharmacotherapy. 2020 May;40(5):438-454. doi: 10.1002/phar.2388. Epub 2020 May 4. Pharmacotherapy. 2020. PMID: 32239518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol Ameliorates Vancomycin-Induced Testicular Dysfunction in Male Rats.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Mar 1;59(3):486. doi: 10.3390/medicina59030486. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36984488 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effect of Omeprazole on Vancomycin Cytotoxicity in HK-2 Cells and Renal Injury in Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2025 Jul 31;2025:3520935. doi: 10.1155/bmri/3520935. eCollection 2025. Biomed Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40900905 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of N-acetylcysteine on apoptosis and NGF-Akt/Bad pathway in the hippocampus tissue of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in male rats.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jun 6;40(5):217. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01641-7. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40478359
-
Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine against titanium dioxide nanoparticles-induced kidney damage in rats.J Mol Histol. 2025 Mar 19;56(2):112. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10395-6. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40106010
-
Renogrit attenuates Vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in human renal spheroids and in Sprague-Dawley rats by regulating kidney injury biomarkers and creatinine/urea clearance.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 8;18(11):e0293605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293605. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37939153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elyasi S, Khalili H, Dashti-Khavidaki S, Mohammadpour A. Vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: mechanism, incidence, risk factors and special populations. A literature review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;68:1243–55. - PubMed
-
- Park SJ, Lim NR, Park HJ, Yang JW, Kim MJ, Kim K. et al. Evaluation of risk factors for vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40:1328–34. - PubMed
-
- Oktem F, Arslan MK, Ozguner F, Candir O, Yilmaz HR, Ciris M. et al. In vivo evidences suggesting the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: protection by erdosteine. Toxicology. 2005;215:227–33. - PubMed
-
- Xu W, Mao Z, Zhao B, Ni T, Deng S, Yu P. et al. Vitamin C attenuates vancomycin induced nephrotoxicity through the reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation in HK-2 cells. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10:1748–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

