The Emerging Portrait of Glial Cell Line-derived Neurotrophic Factor Family Receptor Alpha (GFRα) in Cancers
- PMID: 35582425
- PMCID: PMC9108399
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.64133
The Emerging Portrait of Glial Cell Line-derived Neurotrophic Factor Family Receptor Alpha (GFRα) in Cancers
Abstract
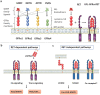
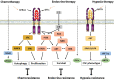
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family receptor alpha (GFRα) members have been widely connected to the mechanisms contributing to cell growth, differentiation, cell migration and tissue maturation. Here we review GFRα biological functions and discussed the evidence indicating whether GFRα signaling complex present novel opportunities for oncogenic intervention and treatment resistance. Thus, our work systematically reviewed the emerging role of GFRα family members in cancers, and provided novel insights for further researches.
Keywords: GDNF; GFRα1; cancer; neural invasion; treatment resistance.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of GFRalpha-3, a novel Co-receptor belonging to the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic receptor family.J Biol Chem. 1998 Feb 6;273(6):3502-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.6.3502. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9452475
-
Evidence for a ligand-specific signaling through GFRalpha-1, but not GFRalpha-2, in the absence of Ret.J Neurosci Res. 2001 Nov 1;66(3):390-5. doi: 10.1002/jnr.1231. J Neurosci Res. 2001. PMID: 11746356
-
Mammalian GFRalpha -4, a divergent member of the GFRalpha family of coreceptors for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family ligands, is a receptor for the neurotrophic factor persephin.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 15;275(50):39427-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003867200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10958791
-
RET-independent signaling by GDNF ligands and GFRα receptors.Cell Tissue Res. 2020 Oct;382(1):71-82. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03261-2. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Cell Tissue Res. 2020. PMID: 32737575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in ischemic brain injury.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 May;962:423-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04086.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12076993 Review.
Cited by
-
The expression patterns of different cell types and their interactions in the tumor microenvironment are predictive of breast cancer patient response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 14:2024.06.14.598770. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.14.598770. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39372749 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Single-Cell Transcriptome Analyses of Four Pain Related Genes in Osteosarcoma.Cancer Inform. 2025 Jul 19;24:11769351251331508. doi: 10.1177/11769351251331508. eCollection 2025. Cancer Inform. 2025. PMID: 40686838 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Neural Environment in Cancer: Exploring the Role of Neural Circuit Players and Potential Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2023 Aug 3;12(15):1996. doi: 10.3390/cells12151996. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37566075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of CRISPRa-mediated gdnf overexpression in an In vitro Parkinson's disease model.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 8;12:1420183. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1420183. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39175618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mulligan LM. RET revisited: expanding the oncogenic portfolio. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:173–86. - PubMed
-
- Kawai K, Takahashi M. Intracellular RET signaling pathways activated by GDNF. Cell and tissue research. 2020;382:113–23. - PubMed
-
- Baloh RH, Tansey MG, Lampe PA, Fahrner TJ, Enomoto H, Simburger KS. et al. Artemin, a novel member of the GDNF ligand family, supports peripheral and central neurons and signals through the GFRalpha3-RET receptor complex. Neuron. 1998;21:1291–302. - PubMed
-
- Sidorova YA, Matlik K, Paveliev M, Lindahl M, Piranen E, Milbrandt J. et al. Persephin signaling through GFRalpha1: the potential for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Molecular and cellular neurosciences. 2010;44:223–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

