Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Turkish version of the sinus and nasal quality of life survey (SN-5)
- PMID: 35582511
- PMCID: PMC9039634
- DOI: 10.14744/nci.2021.94547
Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Turkish version of the sinus and nasal quality of life survey (SN-5)
Abstract
Objective: The Sinus and Nasal Quality of Life (QoL) Survey (SN-5) is a valid questionnaire that evaluates the QoL of the pediatric population associated with sinonasal diseases and symptoms. The aims of this study were to translate the SN-5 test to Turkish language (SN-5t), evaluate the internal consistency of the test and test-retest reliability and validate the translation for further use in studies in Turkish language.
Methods: In this prospective study, 50 healthy subjects and 50 patients, age between 2 and 12, with sinonasal symptoms prolonged over 1 month were included to the study. Families of healthy subjects were asked to fill the SN-5t twice with 1-week interval. The patient group completed test once prior the treatment and once 4 weeks after the treatment. Cronbach's test was performed to test internal consistency and Spearman's test was performed to evaluate test-retest validity.
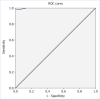
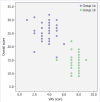
Results: The median value of the pre-treatment tests of the patient group and control group was 25 (23-28) and 14.25 (12-16), respectively. A statistically significant difference was found between groups (p<0.001). Area under the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve (Aroc) value was calculated as 0.992 which stated the strong diagnostic accuracy, and the cutoff point was defined as 16.5. Cronbach's alpha value of 0.75 was found. The Spearman's rank correlation coefficient value (Spearman's rho) was calculated as 0.946.
Conclusion: The Turkish translation of the SN-5 is a consistent and valid test with high sensitivity and specificity that can be used in studies including Turkish speaking population.
Keywords: Pediatrics; Turkish; quality of life; rhinitis; sinusitis; validation studies.
Copyright © 2022 by Istanbul Provincial Directorate of Health - Available online at www.northclinist.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Turkish Translation and Validation of Chronic Otitis Media Questionnaire-12.Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Mar;57(1):24-29. doi: 10.5152/tao.2019.3693. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31049249 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Sinus and Nasal Quality of Life Survey (SN-5) into Brazilian Portuguese.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Nov-Dec;82(6):636-642. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2015.11.013. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26968622 Free PMC article.
-
French translation and validation of the Sinus and Nasal Quality of Life Survey (SN-5) in children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Jun;145:110706. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2021.110706. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33862327
-
Validity and reliability of the Turkish version of caregiver self-assessment questionnaire.Disabil Rehabil. 2020 Nov;42(22):3250-3255. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2019.1587525. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Disabil Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 30990351
-
Food-related quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease: measuring the validity and reliability of the Turkish version of FR-QOL-29.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022 Jul 5;20(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-02014-9. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 35790989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Translation and Validation of the Sinus and Nasal Quality of Life Surgery Survey in Serbian.OTO Open. 2024 Apr 23;8(2):e129. doi: 10.1002/oto2.129. eCollection 2024 Apr-Jun. OTO Open. 2024. PMID: 38654842 Free PMC article.
-
Content Validity of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Developed for Assessing Disease-Specific Quality of Life in Children With Sinonasal Disease: A Systematic Review.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025 Mar;15(3):317-327. doi: 10.1002/alr.23539. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025. PMID: 39968608 Free PMC article.
-
Response to letter to the editor regarding "Sinonasal quality of life in primary ciliary dyskinesia".Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2024 Mar;14(3):749. doi: 10.1002/alr.23297. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2024. PMID: 37937377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Settipane RA, Lieberman P. Update on nonallergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;86:494–507. - PubMed
-
- Seidman MD, Gurgel RK, Lin SY, Schwartz SR, Baroody FM, Bonner JR, et al. Guideline Otolaryngology Development Group AAO-HNSF. Clinical practice guideline: Allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;152:S1–43. - PubMed
-
- Fayers PM, Machin D. Quality of Life. West Sussex: John Wiley; 2007. How to measure quality of life? In: Fayers PM, Machin D, editors. pp. 3–30.
-
- Piccirillo JF, Merritt MG, Jr, Richards ML. Psychometric and clinimetric validity of the 20-Item Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT-20). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002;126:41–7. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins C, Gillett S, Slack R, Lund VJ, Browne JP. Psychometric validity of the 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test. Clin Otolaryngol. 2009;34:447–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources