Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35582540
- PMCID: PMC8992585
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2021.102
Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) mutation are associated with significant clinical heterogeneity and a poor prognosis to standard NSCLC therapies such as surgical resection, radiotherapy, chemotherapies, and targeted medicines. However, the application of immune checkpoints inhibitors (ICIs) has dramatically altered the therapeutic pattern of NSCLC management. Clinical studies have indicated that some KRAS-mutant NSCLC patients could benefit from ICIs; however, the responses in some patients are still poor. This review intends to elucidate the mechanisms of resistance to immunotherapy in KRAS-driven NSCLC and highlight the TME functions altered by immunoinhibitors, immunostimulators, and cancer metabolism. These metabolic pathways could potentially be promising approaches to overcome immunotherapy resistance.
Keywords: KRAS mutation; Non-small cell lung cancer; cancer metabolism.; immune checkpoints inhibitors; tumor microenvironments.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
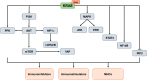
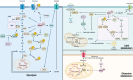
References
-
- Shepherd FA, Lacas B, Le Teuff G, et al. LACE-Bio Collaborative Group. Pooled analysis of the prognostic and predictive effects of TP53 comutation status combined with KRAS or EGFR mutation in early-stage resected non-small-cell lung cancer in four trials of adjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:2018–27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.2893. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
