Emerging role of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in the mechanism of action and resistance to anticancer therapies
- PMID: 35582567
- PMCID: PMC8992506
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2019.57
Emerging role of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in the mechanism of action and resistance to anticancer therapies
Abstract
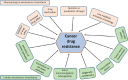
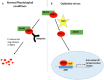
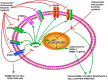
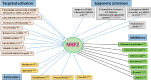
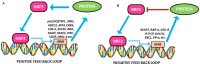
Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (NRF2), a transcription factor, is a master regulator of an array of genes related to oxidative and electrophilic stress that promote and maintain redox homeostasis. NRF2 function is well studied in in vitro, animal and general physiology models. However, emerging data has uncovered novel functionality of this transcription factor in human diseases such as cancer, autism, anxiety disorders and diabetes. A key finding in these emerging roles has been its constitutive upregulation in multiple cancers promoting pro-survival phenotypes. The survivability pathways in these studies were mostly explained by classical NRF2 activation involving KEAP-1 relief and transcriptional induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) neutralizing and cytoprotective drug-metabolizing enzymes (phase I, II, III and 0). Further, NRF2 status and activation is associated with lowered cancer therapeutic efficacy and the eventual emergence of therapeutic resistance. Interestingly, we and others have provided further evidence of direct NRF2 regulation of anticancer drug targets like receptor tyrosine kinases and DNA damage and repair proteins and kinases with implications for therapy outcome. This novel finding demonstrates a renewed role of NRF2 as a key modulatory factor informing anticancer therapeutic outcomes, which extends beyond its described classical role as a ROS regulator. This review will provide a knowledge base for these emerging roles of NRF2 in anticancer therapies involving feedback and feed forward models and will consolidate and present such findings in a systematic manner. This places NRF2 as a key determinant of action, effectiveness and resistance to anticancer therapy.
Keywords: Cancer; DNA damage and repair response; anticancer therapeutics; drug resistance; nuclear factor E2-related factor 2; receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor; targeted therapy.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging role of NRF2 in chemoresistance by regulating drug-metabolizing enzymes and efflux transporters.Drug Metab Rev. 2016 Nov;48(4):541-567. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2016.1197239. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Drug Metab Rev. 2016. PMID: 27320238 Review.
-
Oxidative Stress, Nrf2, and Epigenetic Modification Contribute to Anticancer Drug Resistance.Toxicol Res. 2017 Jan;33(1):1-5. doi: 10.5487/TR.2017.33.1.001. Epub 2017 Jan 15. Toxicol Res. 2017. PMID: 28133507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel mechanism of action of HER2 targeted immunotherapy is explained by inhibition of NRF2 function in ovarian cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75874-75901. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12425. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713148 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2 (NF-E2) p45-related factor 2 interferes with homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2/p53 activity to impair solid tumors chemosensitivity.IUBMB Life. 2020 Aug;72(8):1634-1639. doi: 10.1002/iub.2334. Epub 2020 Jun 27. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32593231
-
Crosstalk between NRF2 and Dicer through metastasis regulating MicroRNAs; mir-34a, mir-200 family and mir-103/107 family.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Jun 15;686:108326. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108326. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32142889 Review.
Cited by
-
An overview of potential of natural compounds to regulate epigenetic modifications in colorectal cancer: a recent update.Epigenetics. 2025 Dec;20(1):2491316. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2025.2491316. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40239010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response and Drug Efflux Transporters Upregulation as Possible Mechanisms of Resistance in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancers.Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Aug 5;17:605-627. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S457749. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 39131905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TMED2 Induces Cisplatin Resistance in Breast Cancer via Targeting the KEAP1-Nrf2 Pathway.Curr Med Sci. 2023 Oct;43(5):1023-1032. doi: 10.1007/s11596-023-2777-7. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Curr Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37615927
-
Assessment of the Oxidative Damage and Genotoxicity of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Exploring the Protective Role of Holy Basil Oil Nanoemulsions in Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Mar;201(3):1301-1316. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03228-0. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 35416606 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoencapsulation of basil essential oil alleviates the oxidative stress, genotoxicity and DNA damage in rats exposed to biosynthesized iron nanoparticles.Heliyon. 2021 Jul 10;7(7):e07537. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07537. eCollection 2021 Jul. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34345731 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
