Targeting the "undruggable" RAS - new strategies - new hope?
- PMID: 35582595
- PMCID: PMC8992515
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2019.21
Targeting the "undruggable" RAS - new strategies - new hope?
Abstract
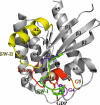
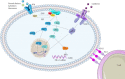
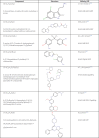
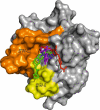
K-RAS is the most frequently mutated oncogene in solid tumors, such as pancreatic, colon or lung cancer. The GTPase K-RAS can either be in an active (GTP-loaded) or inactive (GDP-loaded) form. In its active form K-RAS forwards signals from growth factors, cytokines or hormones to the nucleus, regulating essential pathways, such as cell proliferation and differentiation. In turn, activating somatic mutations of this proto-oncogene deregulate the complex interplay between GAP (GTPase-activating) - and GEF (Guanine nucleotide exchange factor) - proteins, driving neoplastic transformation. Due to a rather shallow surface, K-RAS lacks proper binding pockets for small molecules, hindering drug development over the past thirty years. This review summarizes recent progress in the development of low molecular antagonists and further shows insights of a newly described interaction between mutant K-RAS signaling and PD-L1 induced immunosuppression, giving new hope for future treatments of K-RAS mutated cancer.
Keywords: K-RAS; PD-1; PD-L1; immune checkpoints; small molecules.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Feig LA, Buchsbaum RJ. Cell signaling: life or death decisions of Ras proteins. Curr Biol. 2002;12:259–61. - PubMed
-
- Shields JM, Pruitt K, Shaub A, Der CJ. Understanding Ras : ‘it ain’t over ‘til it’s over’. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:147–54. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer : a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
