The reaction of arteries to haemodialysis - can a change in the cross-sectional area be an important parameter in the assessment of the vessels' condition?
- PMID: 35582602
- PMCID: PMC9093207
- DOI: 10.5114/pjr.2022.115804
The reaction of arteries to haemodialysis - can a change in the cross-sectional area be an important parameter in the assessment of the vessels' condition?
Abstract
Purpose: The objectives of our study were to evaluate the changes in the cross-section area of carotid and femoral arteries caused by fluid loss during haemodialysis (HD) and to determine the direction and amount of these changes.
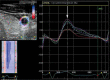
Material and methods: Seventy-four HD patients (28 women and 46 men) were studied. We performed ultrasound exams of the distal common carotid and proximal femoral arteries in each patient before and after a HD session. Recorded exams were analysed using EchoPac software. Arterial cross-section area values were acquired for further analysis.
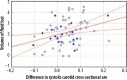
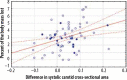
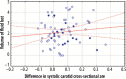
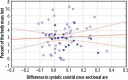
Results: We found a statistically significant decrease in arterial systolic cross-section area values after HD sessions (carotid arteries area before HD equalled 0.6731 cm2 and 0.6333 cm2, p = 0.00001 after HD, femoral arteries area before HD equalled 0.8263 cm2 and 0.7635 cm2, p = 0.00001 after HD). The decrease of systolic carotid cross-section area correlated with the amount of fluid lost during HD sessions (correlation coefficient of 0.3122, p = 0.010) and the percentage of the body mass lost during HD (correlation coefficient of 0.3577, p = 0.003). No statistically significant changes were found in the femoral cross-section area.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that the arterial cross-section area may be used in the assessment of response to body fluid loss. We were able to measure changes due to fluid loss during the HD session. The carotid cross-section values decreased after the procedure and correlated with the amount of fluid lost during the HD session.
Keywords: carotid arteries; femoral artery; haemodynamics; renal dialysis; ultrasonography; vascular stiffness.
Copyright © Polish Medical Society of Radiology 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hoshino J, Fujimoto Y, Naruse Y, et al. Characteristics of revascularization treatment for arteriosclerosis obliterans in patients with and without hemodialysis. Circ J 2010; 74: 2426-2433. - PubMed
-
- Arnett DK, Evans GW, Riley WA. Arterial stiffness: a new cardiovascular risk factor? Am J Epidemiol 1994; 140: 669-682. - PubMed
-
- Chaignon M, Chen WT, Tarazi RC, Bravo EL, Nakamoto S. Effect of hemodialysis on blood volume distribution and cardiac output. Hypertension 1981; 3: 327-332. - PubMed
-
- Tabara Y, Nakura J, Kondo I, Miki T, Kohara K. Orthostatic systolic hypotension and the reflection pressure wave. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 537-543. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
