Non-small cell lung cancer-small cell lung cancer transformation as mechanism of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer
- PMID: 35582610
- PMCID: PMC9090586
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2019.85
Non-small cell lung cancer-small cell lung cancer transformation as mechanism of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer
Abstract
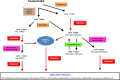
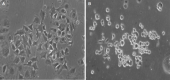
Mutated or rearranged driver kinases in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells are clinically amenable to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) resulting in prolonged survival and significant benefit compared to cytotoxic chemotherapy. The most frequent genomic alterations are observed for epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase, which can be blocked by a range of specific TKIs in sequence. In clinics, resistance to TKIs emerges after approximately one year and comprises secondary mutations of the kinases (on-target) or alternative pathways circumventing the original kinase (off-target) alterations. A special feature of NSCLC is the occurrence of histological transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) in up to 14% of cases, which, in general, is accompanied by resistance to the original TKIs. SCLC transformed tumors may be treated with the classical platinum/etoposide regimen but thus far there are no definitive guidelines. Four transformed pleural SCLC lines in our lab indicate the presence of a gradual NSCLC-SCLC shift with overlapping drug sensitivities. In conclusion, the treatment of NSCLC-SCLC transformed cancer cells would need a better chemosensitivity assessment using functional genomics to guide further therapy.
Keywords: Lung cancer; chemotherapy; drug resistance; epidermal growth factor receptor; non-small cell lung cancer; small cell lung cancer; transformation; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
