Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
- PMID: 35582623
- PMCID: PMC9055171
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2022-0046
Analysis of genetic characteristics of 436 children with dysplasia and detailed analysis of rare karyotype
Abstract
Chromosomal abnormality is one of the important causes of dysplasia in children. However, due to regional and ethnic differences, the reported rates of chromosomal abnormalities in patients with dysplasia vary greatly. Moreover, the clinical manifestations in children with rare chromosomal diseases were heterogeneous. So, we retrospectively analyzed the karyotype results of 436 children with dysplasia and conducted a detailed analysis of rare chromosomal diseases. The results showed that chromosomal abnormalities were present in 181 of 436 cases. Intellectual disability, dysmorphology, congenital malformations, the disorder of sexual development, and short stature were the main five clinical symptoms in children with chromosomal abnormalities. Moreover, 136 cases of Trisomy 21 (Tri21) were detected, of which 130 were standard Tri21, 5 were robertsonian Tri21, and 1 was chimera type. In addition, 16 cases of rare abnormal karyotype, including complex Tri21, complex Turner syndrome, 4p-syndrome, 18q-syndrome, and 5p-syndrome, were also detected. In summary, chromosome abnormality is one of the important causes of dysplasia in children. Furthermore, prenatal screening and diagnosis could play a great significance in preventing dysplasia in children. In addition, the retrospective analysis of rare cases is valuable for clinical diagnosis and risk assessment of recurrence.
Keywords: 18q-syndrome; 4q-syndrome; dysplasia; monomer 9p; trilogy 21.
© 2022 Zong-Yu Miao et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
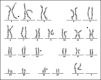
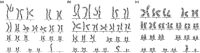
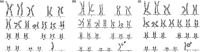
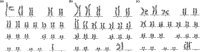
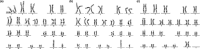

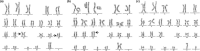
Similar articles
-
Cytogenetic analysis of 2959 couples with spontaneous abortion and detailed analysis of rare karyotypes.J Genet. 2022;101:10. J Genet. 2022. PMID: 35129129
-
Postnatal Identification of Trisomy 21: An Overview of 7,133 Postnatal Trisomy 21 Cases Identified in a Diagnostic Reference Laboratory in China.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0133151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133151. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26176847 Free PMC article.
-
[Karyotype analysis of amniotic fluid cells and comparison of chromosomal abnormality rate during second trimester].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2011 Sep;46(9):644-8. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22176986 Chinese.
-
[Analysis of the chromosomal abnormality in 5774 patients with clinical reproductive abnormality and 32 new karyotypes].Yi Chuan. 2009 Feb;31(2):142-6. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2009.00142. Yi Chuan. 2009. PMID: 19273421 Review. Chinese.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Long-Term Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment of 18q- Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 9;12:776835. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.776835. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34956087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hartman RJ, Rasmussen SA, Botto LD, Riehle-Colarusso T, Martin CL, Cragan JD, et al. The contribution of chromosomal abnormalities to congenital heart defects: a population-based study. Pediatr Cardiol. 2011;32:1147–57. - PubMed
-
- Huang Z, Sun Y, Fan Y, Wang L, Liu H, Gong Z, et al. Genetic evaluation of 114 Chinese short stature children in the next generation era: a single center study. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49:295–305. - PubMed
-
- Szabó A, Czakó M, Hadzsiev K, Duga B, Bánfai Z, Komlósi K, et al. Small supernumerary marker chromosome 15 and a ring chromosome 15 associated with a 15q26.3 deletion excluding the IGF1R gene. Am J Med Genet A. 2018;176:443–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
