Explainable artificial intelligence-based edge fuzzy images for COVID-19 detection and identification
- PMID: 35582662
- PMCID: PMC9102011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108966
Explainable artificial intelligence-based edge fuzzy images for COVID-19 detection and identification
Abstract
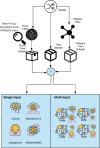
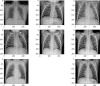
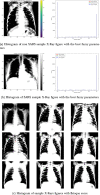
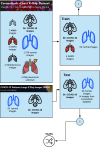
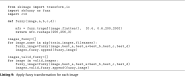
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to wreak havoc on the world's population's health and well-being. Successful screening of infected patients is a critical step in the fight against it, with radiology examination using chest radiography being one of the most important screening methods. For the definitive diagnosis of COVID-19 disease, reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction remains the gold standard. Currently available lab tests may not be able to detect all infected individuals; new screening methods are required. We propose a Multi-Input Transfer Learning COVID-Net fuzzy convolutional neural network to detect COVID-19 instances from torso X-ray, motivated by the latter and the open-source efforts in this research area. Furthermore, we use an explainability method to investigate several Convolutional Networks COVID-Net forecasts in an effort to not only gain deeper insights into critical factors associated with COVID-19 instances, but also to aid clinicians in improving screening. We show that using transfer learning and pre-trained models, we can detect it with a high degree of accuracy. Using X-ray images, we chose four neural networks to predict its probability. Finally, in order to achieve better results, we considered various methods to verify the techniques proposed here. As a result, we were able to create a model with an AUC of 1.0 and accuracy, precision, and recall of 0.97. The model was quantized for use in Internet of Things devices and maintained a 0.95 percent accuracy.
Keywords: COVID-19; Intern of Things; Multi-input convolutional network; Soft computing; X-ray; XAI.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







Similar articles
-
COVID-Net: a tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 11;10(1):19549. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76550-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33177550 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-DSNet: A novel deep convolutional neural network for detection of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) cases from CT and Chest X-Ray images.Artif Intell Med. 2022 Dec;134:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102427. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Artif Intell Med. 2022. PMID: 36462906 Free PMC article.
-
TB-Net: A Tailored, Self-Attention Deep Convolutional Neural Network Design for Detection of Tuberculosis Cases From Chest X-Ray Images.Front Artif Intell. 2022 Apr 7;5:827299. doi: 10.3389/frai.2022.827299. eCollection 2022. Front Artif Intell. 2022. PMID: 35464996 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-Net L2C-ULTRA: An Explainable Linear-Convex Ultrasound Augmentation Learning Framework to Improve COVID-19 Assessment and Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 4;24(5):1664. doi: 10.3390/s24051664. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475199 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A tree-based explainable AI model for early detection of Covid-19 using physiological data.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024 Jun 24;24(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02576-2. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024. PMID: 38915001 Free PMC article.
-
ROI extraction in corona virus (COVID 19) CT images using intuitionistic fuzzy edge detection.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 16;10(6):e27798. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27798. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38545231 Free PMC article.
-
Explaining COVID-19 diagnosis with Taylor decompositions.Neural Comput Appl. 2022 Nov 17:1-14. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-08021-7. Online ahead of print. Neural Comput Appl. 2022. PMID: 36415284 Free PMC article.
-
Feature Extraction Approach for Speaker Verification to Support Healthcare System Using Blockchain Security for Data Privacy.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jul 25;2022:8717263. doi: 10.1155/2022/8717263. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35924113 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic COVID-19 and Common-Acquired Pneumonia Diagnosis Using Chest CT Scans.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Apr 26;10(5):529. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10050529. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Basset M., Mohamed R., Elhoseny M., Chakrabortty R.K., Ryan M. A hybrid COVID-19 detection model using an improved marine predators algorithm and a ranking-based diversity reduction strategy. IEEE Access. 2020;8:79521–79540. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990893. - DOI
-
- Ng H.P., Ong S.H., Foong K.W.C., Goh P.S., Nowinski W.L. 2006 IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation. 2001. Medical image segmentation using k-means clustering and improved watershed algorithm view project neuro vasculature modeling view project medical image segmentation using k-means clustering and improved watershed algorithm; pp. 61–65. URL https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4243554. - DOI
-
- Shi F., Wang J., Shi J., Wu Z., Wang Q., Tang Z., He K., Shi Y., Shen D. Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation and diagnosis for COVID-19. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020;3333(c):1–13. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2020.2987975. arXiv:2004.02731. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santos M.A., Munoz R., Olivares R., Rebouças Filho P.P., Del Ser J., de Albuquerque V.H.C. Online heart monitoring systems on the internet of health things environments: A survey, a reference model and an outlook. Inf. Fusion. 2020;53:222–239.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
