Clinical classification of symptomatic heterotopic pancreas of the stomach and duodenum: A case series and systematic literature review
- PMID: 35582670
- PMCID: PMC9048474
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1455
Clinical classification of symptomatic heterotopic pancreas of the stomach and duodenum: A case series and systematic literature review
Abstract
Background: Heterotopic pancreas (HP) is an aberrant anatomic malformation that occurs most commonly in the upper gastrointestinal tract. While the majority of heterotopic pancreatic lesions are asymptomatic, many manifest severe clinical symptoms which require surgical or endoscopic intervention. Understanding of the clinical manifestations and symptoms of HP is limited due to the lack of large volume studies in the literature. The purpose of this study is to review symptomatic cases at a single center and compare these to a systematic review of the literature in order to characterize common clinical manifestations and treatment of this disease.
Aim: To classify the common clinical manifestations of heterotopic pancreas.
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted of pathologic samples containing heterotopic pancreas from 2000-2018. Review was limited to HP of the upper gastrointestinal tract due to the frequency of presentation in this location. Symptomatic patients were identified from review of the medical records and clinical symptoms were tabulated. These were compared to a systematic review of the literature utilizing PubMed and Embase searches for papers pertaining to heterotopic pancreas. Publications describing symptomatic presentation of HP were selected for review. Information including demographics, symptoms, presentation and treatment were compiled and analyzed.
Results: Twenty-nine patient were identified with HP at a single center, with six of these identified has having clinical symptoms. Clinical manifestations included, gastrointestinal bleeding, gastric ulceration with/without perforation, pancreatitis, and gastric outlet obstruction. Systemic review of the literature yielded 232 publications detailing symptomatic cases with only 20 studies describing ten or more patients. Single and multi-patient studies were combined to form a cohort of 934 symptomatic patients. The majority of patients presented with abdominal pain (67%) combined with one of the following clinical categories: (1) Dyspepsia, (n = 445, 48%); (2) Pancreatitis (n = 260, 28%); (3) Gastrointestinal bleeding (n = 80, 9%); and (4) Gastric outlet obstruction (n = 80, 9%). The majority of cases (n = 832, 90%) underwent surgical or endoscopic resection with 85% reporting resolution or improvement in their symptoms.
Conclusion: Heterotopic pancreas can cause significant clinical symptoms in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Better understanding and classification of this disease may result in more accurate identification and treatment of this malformation.
Keywords: Aberrant pancreas; Ectopic pancreas; Groove pancreatitis; Heterotopic pancreas; Pancreatic rest.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors of this study have no related conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

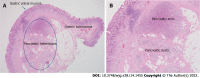
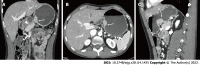
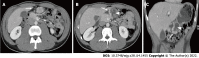

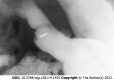
References
-
- De Castro Barboso J, Waugh JM. Heterotopic pancreatic tissue, clinically significant, in the gastric wall of a boy six years of age. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1947;22:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberger CF, Gocht A, Knoefel WT, Busch CB, Peiper M, Kutup A, Yekebas EF, Hosch SB, Lambrecht W, Izbicki JR. Heterotopic pancreas--clinical presentation and pathology with review of the literature. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004;51:854–858. - PubMed
-
- Ormarsson OT, Gudmundsdottir I, Mårvik R. Diagnosis and treatment of gastric heterotopic pancreas. World J Surg. 2006;30:1682–1689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

