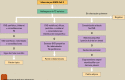
[Diagnostic protocol for febrile lung infiltrates during the COVID-19 pandemic]
- PMID: 35582697
- PMCID: PMC9098090
- DOI: 10.1016/j.med.2022.05.009
[Diagnostic protocol for febrile lung infiltrates during the COVID-19 pandemic]
Abstract
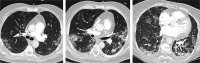
Chest x-ray and computed tomography (CT) scans are important pillars for the diagnosis of lung involvement in COVID-19. The radiological image is typically characterized by peripheral, bilateral ground glass opacities (GGO), mainly located in the lower lobes. The limited sensitivity and specificity of these imaging techniques and possible atypical morphological or topographical presentations make it necessary to always rule out other infectious and non-infectious diseases. Therefore, it is fundamental to consider the patient's clinical and analytical data and the epidemiological circumstances.
La radiografía de tórax y la tomografía computarizada (TC) son pilares importantes para el diagnóstico de la afectación pulmonar en la COVID-19, con una imagen radiológica caracterizada típicamente por opacidades en vidrio deslustrado (OVD) periféricas, bilaterales y localizadas principalmente en lóbulos inferiores. La sensibilidad y la especificidad limitada de estas técnicas de imagen y las posibles presentaciones morfológicas o topográficas atípicas obligan a descartar siempre otras patologías tanto infecciosas como no infecciosas, para lo que es fundamental considerar los datos clínicos y analíticos del paciente y las circunstancias epidemiológicas.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest x-ray; Computed tomography; Differential diagnosis.
.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
