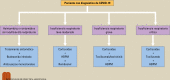
[Treatment protocol for COVID-19 in patients with and without an indication for hospital admission]
- PMID: 35582698
- PMCID: PMC9097963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.med.2022.05.005
[Treatment protocol for COVID-19 in patients with and without an indication for hospital admission]
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 infection causes a wide spectrum of symptoms with varying degrees of severity, from asymptomatic cases or cases in the form of self-limiting influenza-like illness to cases of rapidly progressing respiratory distress syndrome due to an anomalous immune system response in the form of a cytokine storm. Thrombotic complications are also common. Multiple antiviral treatments have been tested in COVID-19 without favorable outcomes. Only remdesivir may be useful, but not in all cases, and its use is controversial. On the contrary, immunomodulating treatments have the most solid evidence, particularly glucocorticoids. Other more specific immunosuppressors, such as interleukin-6 inhibitors, have also shown favorable results and many others are currently being studied. Thromboprophylaxis is the other pillar of COVID-19 treatment, although the anticoagulant dose to be used is still being discussed.
La infeccion por SARS-CoV-2 causa un amplio espectro de sintomas con distintos grados de severidad; desde casos asintomaticos o en forma de sindrome pseudogripal autolimitado, hasta un sindrome de distres respiratorio rapidamente progresivo debido a una respuesta anomala del sistema inmunitario en forma de tormenta de citoquinas. Tambien son frecuentes las complicaciones tromboticas. Multiples tratamientos antivirales se han probado en la COVID-19 sin resultados favorables, tan solo remdesivir puede ser util, pero no en todos los casos, y su uso es controvertido. Por el contrario, son los tratamientos inmunomoduladores los que mas solida evidencia de beneficio han acumulado, particularmente los corticoides. Otros inmunosupresores mas especificos, como los inhibidores de la interleuquina 6, tambien han logrado resultados favorables, y muchos otros estan actualmente en estudio. La tromboprofilaxis es el otro pilar del tratamiento de la COVID-19, aunque la dosis anticoagulante a emplear todavia esta en discusion.
Keywords: Glucocorticoids; Low-molecular-weight heparin; Remdesivir; Tocilizumab.
.
Figures
References
-
- fx5 Yu L.M., Bafadhel M., Dorward J., Hayward G., Saville B.R., Gbinigie O., et al. PRINCIPLE Trial Collaborative Group. Inhaled budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10303):843–855. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous