Immediate post-exercise blood pressure and arterial stiffness in hypertensive and normotensive older females
- PMID: 35582956
- PMCID: PMC9180321
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.14490
Immediate post-exercise blood pressure and arterial stiffness in hypertensive and normotensive older females
Abstract
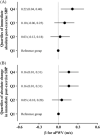
Although it has been suggested that increased arterial stiffness is linked to exaggerated blood pressure (BP) from brief moderate exercise, it is not clear whether this occurs in older adults with and without hypertension. This study investigates whether the immediate post-exercise systolic BP following brief moderate exercise is associated with arterial stiffness in older females with different BP status. This cross-sectional study included 191 older females aged 60-80 years without known cardiovascular disease (CVD). Arterial stiffness was determined by aortic pulse wave velocity (aPWV). Systolic BP was measured before and immediately following a 3-min moderate walking test (stage 1 Bruce protocol). Specific quartile-based thresholds were used to define an exaggerated immediate post-exercise systolic BP for hypertensive and normotensive older females (quartile 4 as an exaggerated response). Traditional CVD risk factors were assessed (covariates). Older females from the highest quartile of immediate post-exercise absolute systolic BP showed higher aPWV compared to their peers from the lowest quartile (β = .22 m/s, p = .018). The quartile-based threshold to define the exaggerated post-exercise systolic BP was higher in hypertensive than in normotensive older females (174 vs. 172 mmHg). In summary, exaggerated immediate post-exercise systolic BP following a brief moderate exercise is associated with higher arterial stiffness in older females with different BP status.
Keywords: aging; arterial compliance; exaggerated exercise blood pressure; exercise-induced hypertension; pulse wave velocity; vascular health.
© 2022 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Fondation de l'Hôpital Saint-Boniface
- 306744/2019-8/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- 307293/2019-0/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- 427729/2018-1/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

