MicroRNAs in peripheral artery disease: potential biomarkers and pathophysiological mechanisms
- PMID: 35583375
- PMCID: PMC9121511
- DOI: 10.1177/17539447221096940
MicroRNAs in peripheral artery disease: potential biomarkers and pathophysiological mechanisms
Abstract
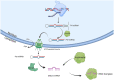
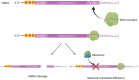
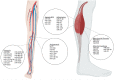
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a disease of atherosclerosis in the lower extremities. PAD carries a massive burden worldwide, while diagnosis and treatment options are often lacking. One of the key points of research in recent years is the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs), which are short 20-25 nucleotide single-stranded RNAs that can act as negative regulators of post-transcriptional gene expression. Many of these miRNAs have been discovered to be misregulated in PAD patients, suggesting a potential utility as biomarkers for PAD diagnosis. miRNAs have also been shown to play an important role in many different pathophysiological aspects involved in the initiation and progression of the disease including angiogenesis, hypoxia, inflammation, as well as other cellular functions like cell proliferation and migration. The research on miRNAs in PAD has the potential to lead to a whole new class of diagnostic tools and treatments.
Keywords: angiogenesis; biomarkers; critical limb ischemia; hypoxia; intermittent claudication; non-coding RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory and Prothrombotic Biomarkers, DNA Polymorphisms, MicroRNAs and Personalized Medicine for Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12054. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912054. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-548j-5p regulates angiogenesis in peripheral artery disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 17;12(1):838. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-04770-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35039547 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs in peripheral artery disease - something gripping this way comes.Vasa. 2014 May;43(3):163-70. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000345. Vasa. 2014. PMID: 24797047 Review.
-
Peripheral artery disease: a micro-RNA-related condition?Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;39:105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29679926 Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in peripheral artery disease (review).Mol Med Rep. 2012 Oct;6(4):695-700. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.978. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 22767222 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Profiling in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia Their Role in Arteriogenesis.Int J Angiol. 2025 Jan 13;34(2):83-91. doi: 10.1055/a-2504-1911. eCollection 2025 Jun. Int J Angiol. 2025. PMID: 40365156
-
Unveiling vital biomarkers and immune infiltration profiles in endoplasmic reticulum stress following spinal cord injury.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 2;14(1):29981. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81844-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39623003 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative Review of Biological Markers in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 3;12(4):798. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040798. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cell dysfunction: Implications for the pathogenesis of peripheral artery disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Nov 16;9:1054576. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1054576. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36465438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paired Transcriptomic Analyses of Atheromatous and Control Vessels Reveal Novel Autophagy and Immunoregulatory Genes in Peripheral Artery Disease.Cells. 2024 Jul 28;13(15):1269. doi: 10.3390/cells13151269. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kullo IJ, Rooke TW. Peripheral artery disease. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 861–871. - PubMed
-
- Song P, Rudan D, Zhu Y, et al.. Global, regional, and national prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2015: an updated systematic review and analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2019; 7: e1020–e1030. - PubMed
-
- Gardner AW. Claudication pain and hemodynamic responses to exercise in younger and older peripheral arterial disease patients. J Gerontol 1993; 48: M231–M236. - PubMed
-
- Mascarenhas JV, Albayati MA, Shearman CP, et al.. Peripheral arterial disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2014; 43: 149–166. - PubMed
-
- Hamburg NM, Creager MA. Pathophysiology of intermittent claudication in peripheral artery disease. Circ J 2017; 81: 281–289. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

