The cardiosplenic axis: the prognostic role of the spleen in heart failure
- PMID: 35583622
- PMCID: PMC9546960
- DOI: 10.1007/s10741-022-10248-4
The cardiosplenic axis: the prognostic role of the spleen in heart failure
Abstract
Despite the number of available methods to predict prognosis in patients with heart failure, prognosis remains poor, likely because of marked patient heterogeneity and varied heart failure etiologies. Thus, identification of novel prognostic indicators to stratify risk in patients with heart failure is of paramount importance. The spleen is emerging as a potential novel prognostic indicator for heart failure. In this article, we provide an overview of the current prognostic tools used for heart failure. We then introduce the spleen as a potential novel prognostic indicator, before outlining the structure and function of the spleen and introducing the concept of the cardiosplenic axis. This is followed by a focused discussion on the function of the spleen in the immune response and in hemodynamics, as well as a review of what is known about the usefulness of the spleen as an indicator of heart failure. Expert insight into the most effective spleen-related measurement indices for the prognostication of patients with heart failure is provided, and suggestions on how these could be measured in clinical practice are considered. In future, studies in humans will be required to draw definitive links between specific splenic measurements and different heart failure manifestations, as well as to determine whether splenic prognostic measurements differ between heart failure classes and etiologies. These contributions will provide a step forward in our understanding of the usefulness of the spleen as a prognostic predictor in heart failure.
Keywords: Cardiosplenic axis; Heart failure; Hemodynamics; Immunity; Prognosis; Spleen.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Takahiro Okumura received research grants from Ono Pharmaceutical, Bayer Pharmaceutical, Daiichi-Sankyo Pharma, and Amgen Astellas BioPharma, as well as honoraria from Ono Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Novartis Pharma, and Medtronic Japan. Toyoaki Murohara received lecture fees from Bayer Pharmaceutical, Daiichi-Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Kowa, MSD, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma, Pfizer Japan, Sanofi-Aventis, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. Toyoaki Murohara also received an unrestricted research grant from the Department of Cardiology of Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, as well as honoraria from Astellas Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Kowa, MSD, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma, Otsuka Pharma, Pfizer Japan, Sanofi-Aventis, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Teijin Pharma. All other authors declare that they have no relationships with industry relevant to the contents of this paper.
Figures
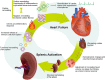
Similar articles
-
Heart functional and structural compendium of cardiosplenic and cardiorenal networks in acute and chronic heart failure pathology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):H255-H267. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00528.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29101178 Free PMC article.
-
Splenic size as an indicator of hemodynamics and prognosis in patients with heart failure.Heart Vessels. 2022 Aug;37(8):1344-1355. doi: 10.1007/s00380-022-02030-1. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Heart Vessels. 2022. PMID: 35092456
-
The cardiosplenic axis: another obscure pathophysiological function of the spleen and its investigation using molecular imaging.Nucl Med Commun. 2017 Mar;38(3):205-208. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000635. Nucl Med Commun. 2017. PMID: 28009777 Review.
-
Remodeling of the mononuclear phagocyte network underlies chronic inflammation and disease progression in heart failure: critical importance of the cardiosplenic axis.Circ Res. 2014 Jan 17;114(2):266-82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301720. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24186967 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid profiling to predict prognosis in patients with heart failure: an expert review.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Feb;10(1):32-43. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14222. Epub 2022 Oct 27. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36300549 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spleen-Derived CCL9 Recruits MDSC to Facilitate Tumor Growth in Orthotopic Hepatoma Mice.Glob Med Genet. 2023 Dec 1;10(4):348-356. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1777327. eCollection 2023 Dec. Glob Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 38046278 Free PMC article.
-
Multidetector CT Imaging Biomarkers as Predictors of Prognosis in Shock: Updates and Future Directions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;13(13):2304. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132304. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T Cells Boost Efficacy of Post-Infarction Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiovascular Progenitor Cell Transplants.Cells. 2025 Jun 23;14(13):956. doi: 10.3390/cells14130956. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40643477 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Left Ventricular Dysfunction from Cardiomyopathies to Myocardial Viability: When and Why Cardiac Function Recovers.Biomedicines. 2024 May 9;12(5):1051. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051051. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of the heart, spleen, and bone marrow in heart failure: the role of splenic extramedullary hematopoiesis.Heart Fail Rev. 2024 Sep;29(5):1049-1063. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10418-6. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Heart Fail Rev. 2024. PMID: 38985383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (2021) Cardiovascular disease. https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases/#tab=tab_1. Accessed 23 July 2021
-
- Lippi G, Sanchis-Gomar F (2020) Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med J 5. 10.21037/amj.2020.03.03
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

