Transcriptional Repression by FoxM1 Suppresses Tumor Differentiation and Promotes Metastasis of Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35583996
- PMCID: PMC9258028
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0410
Transcriptional Repression by FoxM1 Suppresses Tumor Differentiation and Promotes Metastasis of Breast Cancer
Abstract
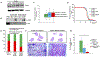
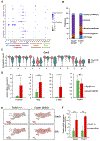
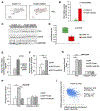
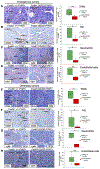
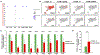
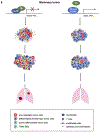
The transcription factor Forkhead box M1 (FoxM1) is overexpressed in breast cancers and correlates with poor prognosis. Mechanistically, FoxM1 associates with CBP to activate transcription and with Rb to repress transcription. Although the activating function of FoxM1 in breast cancer has been well documented, the significance of its repressive activity is poorly understood. Using CRISPR-Cas9 engineering, we generated a mouse model that expresses FoxM1-harboring point mutations that block binding to Rb while retaining its ability to bind CBP. Unlike FoxM1-null mice, mice harboring Rb-binding mutant FoxM1 did not exhibit significant developmental defects. The mutant mouse line developed PyMT-driven mammary tumors that were deficient in lung metastasis, which was tumor cell-intrinsic. Single-cell RNA-seq of the tumors revealed a deficiency in prometastatic tumor cells and an expansion of differentiated alveolar type tumor cells, and further investigation identified that loss of the FoxM1/Rb interaction caused enhancement of the mammary alveolar differentiation program. The FoxM1 mutant tumors also showed increased Pten expression, and FoxM1/Rb was found to activate Akt signaling by repressing Pten. In human breast cancers, expression of FoxM1 negatively correlated with Pten mRNA. Furthermore, the lack of tumor-infiltrating cells in FoxM1 mutant tumors appeared related to decreases in pro-metastatic tumor cells that express factors required for infiltration. These observations demonstrate that the FoxM1/Rb-regulated transcriptome is critical for the plasticity of breast cancer cells that drive metastasis, identifying a prometastatic role of Rb when bound to FoxM1.
Significance: This work provides new insights into how the interaction between FoxM1 and Rb facilitates the evolution of metastatic breast cancer cells by altering the transcriptome.
©2022 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

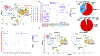
Similar articles
-
FoxM1 regulates mammary luminal cell fate.Cell Rep. 2012 Jun 28;1(6):715-29. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.05.005. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 22813746 Free PMC article.
-
Thiostrepton selectively targets breast cancer cells through inhibition of forkhead box M1 expression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jul;7(7):2022-32. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0188. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18645012
-
FoxM1 is a downstream target and marker of HER2 overexpression in breast cancer.Int J Oncol. 2009 Jul;35(1):57-68. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000313. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19513552 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the oncogenic transcription factor FOXM1 to improve outcomes in all subtypes of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 27;25(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01675-8. Breast Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37370117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOX(M1) news--it is cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Mar;12(3):245-54. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0712. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23443798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FOXM1/KIF20A axis promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression via regulating EMT signaling and affects immunotherapy response.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 23;9(12):e22734. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22734. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38125441 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1, MEK, and CDK4/6: New Targets for Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 2;24(17):13596. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713596. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
O-GlcNAcylation: A Crucial Regulator in Cancer-Associated Biological Events.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Sep;81(3):383-394. doi: 10.1007/s12013-023-01146-z. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37392316 Review.
-
Lasalocid inhibits melanoma by down-regulating FOXM1 through PI3K/AKT and JNK/P38 MAPK pathways.J Cancer. 2025 Jan 1;16(3):765-783. doi: 10.7150/jca.101798. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39781349 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation in the tumor microenvironment: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 22;8(1):210. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01480-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37217462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

