Enabling genomic island prediction and comparison in multiple genomes to investigate bacterial evolution and outbreaks
- PMID: 35584003
- PMCID: PMC9465072
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.000818
Enabling genomic island prediction and comparison in multiple genomes to investigate bacterial evolution and outbreaks
Abstract
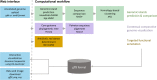
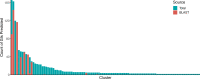
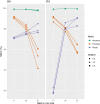
Outbreaks of virulent and/or drug-resistant bacteria have a significant impact on human health and major economic consequences. Genomic islands (GIs; defined as clusters of genes of probable horizontal origin) are of high interest because they disproportionately encode virulence factors, some antimicrobial-resistance (AMR) genes, and other adaptations of medical or environmental interest. While microbial genome sequencing has become rapid and inexpensive, current computational methods for GI analysis are not amenable for rapid, accurate, user-friendly and scalable comparative analysis of sets of related genomes. To help fill this gap, we have developed IslandCompare, an open-source computational pipeline for GI prediction and comparison across several to hundreds of bacterial genomes. A dynamic and interactive visualization strategy displays a bacterial core-genome phylogeny, with bacterial genomes linearly displayed at the phylogenetic tree leaves. Genomes are overlaid with GI predictions and AMR determinants from the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD), and regions of similarity between the genomes are also displayed. GI predictions are performed using Sigi-HMM and IslandPath-DIMOB, the two most precise GI prediction tools based on nucleotide composition biases, as well as a novel blast-based consistency step to improve cross-genome prediction consistency. GIs across genomes sharing sequence similarity are grouped into clusters, further aiding comparative analysis and visualization of acquisition and loss of mobile GIs in specific sub-clades. IslandCompare is an open-source software that is containerized for local use, plus available via a user-friendly, web-based interface to allow direct use by bioinformaticians, biologists and clinicians (at https://islandcompare.ca).
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; comparative genomics; genomic islands; interactive visualization; web server.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved genomic island predictions with IslandPath-DIMOB.Bioinformatics. 2018 Jul 1;34(13):2161-2167. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty095. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29905770 Free PMC article.
-
IslandViewer update: Improved genomic island discovery and visualization.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(Web Server issue):W129-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt394. Epub 2013 May 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23677610 Free PMC article.
-
IslandViewer: an integrated interface for computational identification and visualization of genomic islands.Bioinformatics. 2009 Mar 1;25(5):664-5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp030. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19151094 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial genomic island discovery, visualization and analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Sep 27;20(5):1685-1698. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby042. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29868902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detecting genomic islands using bioinformatics approaches.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 May;8(5):373-82. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2350. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20395967 Review.
Cited by
-
Antarctic Sphingomonas sp. So64.6b showed evolutive divergence within its genus, including new biosynthetic gene clusters.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 18;13:1007225. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1007225. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36466678 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the comparative genome of rice pathogen Burkholderia plantarii: unveiling virulence, fitness traits, and a potential type III secretion system effector.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 23;15:1416253. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1416253. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38845849 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic insights into the taxonomic status and bioactive gene cluster profiling of Bacillus velezensis RVMD2 isolated from desert rock varnish in Ma'an, Jordan.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 24;20(4):e0319345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319345. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40273114 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles.Microorganisms. 2025 May 14;13(5):1129. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13051129. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431301 Free PMC article.
-
zol and fai: large-scale targeted detection and evolutionary investigation of gene clusters.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 24;53(3):gkaf045. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf045. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39907107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freschi L, Bertelli C, Jeukens J, Moore MP, Kukavica-Ibrulj I, et al. Genomic characterisation of an international Pseudomonas aeruginosa reference panel indicates that the two major groups draw upon distinct mobile gene pools. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018;365:fny120. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny120. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

