Pulmonary haemorrhage as the earliest sign of severe leptospirosis in hamster model challenged with Leptospira interrogans strain HP358
- PMID: 35584087
- PMCID: PMC9116642
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010409
Pulmonary haemorrhage as the earliest sign of severe leptospirosis in hamster model challenged with Leptospira interrogans strain HP358
Abstract
Background: Severe leptospirosis is challenging as it could evolve rapidly and potentially fatal if appropriate management is not performed. An understanding of the progression and pathophysiology of Leptospira infection is important to determine the early changes that could be potentially used to predict the severe occurrence of leptospirosis. This study aimed to understand the kinetics pathogenesis of Leptospira interrogans strain HP358 in the hamster model and identify the early parameters that could be used as biomarkers to predict severe leptospirosis.
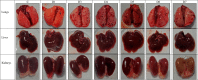
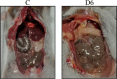
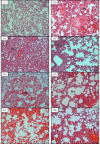
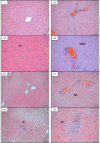
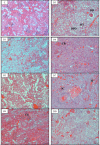
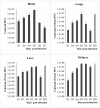
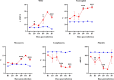
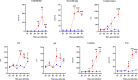
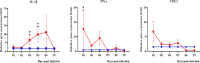
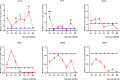
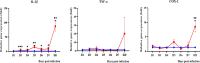
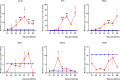
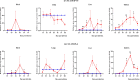
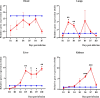
Methodology/principal findings: Male Syrian hamsters were infected with Leptospira interrogans strain HP358 and euthanized after 24 hours, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 days post-infection. Blood, lungs, liver and kidneys were collected for leptospiral detection, haematology, serum biochemistry and differential expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory markers. Macroscopic and microscopic organ damages were investigated. Leptospira interrogans strain HP358 was highly pathogenic and killed hamsters within 6-7 days post-infection. Pulmonary haemorrhage and blood vessel congestion in organs were noticed as the earliest pathological changes. The damages in organs and changes in biochemistry value were preceded by changes in haematology and immune gene expression.
Conclusion/significance: This study deciphered haemorrhage as the earliest manifestation of severe leptospirosis and high levels of IL-1β, CXCL10/IP-10, CCL3/MIP-α, neutrophils and low levels of lymphocytes and platelets serve as a cumulative panel of biomarkers in severe leptospirosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High virulence in hamsters of four dominant Leptospira serovars isolated from rats in the Philippines.Microbiology (Reading). 2014 Feb;160(Pt 2):418-428. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.072439-0. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Microbiology (Reading). 2014. PMID: 24257815
-
Myocarditis and neutrophil-mediated vascular leakage but not cytokine storm associated with fatal murine leptospirosis.EBioMedicine. 2025 Feb;112:105571. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105571. Epub 2025 Jan 30. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39889371 Free PMC article.
-
IL-10 Deficiency Protects Hamsters from Leptospira Infection.Infect Immun. 2022 Feb 17;90(2):e0058421. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00584-21. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 34898251 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospirosis is an invasive infectious and systemic inflammatory disease.Biomed J. 2020 Feb;43(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2019.12.002. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Biomed J. 2020. PMID: 32200953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sigma factors of RNA polymerase in the pathogenic spirochaete Leptospira interrogans, the causative agent of leptospirosis.FASEB J. 2023 Oct;37(10):e23163. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300252RRR. FASEB J. 2023. PMID: 37688587 Review.
Cited by
-
A Paternal Fish Oil Diet Preconception Reduces Lung Inflammation in a Toxicant-Driven Murine Model of New Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.Mar Drugs. 2023 Feb 27;21(3):161. doi: 10.3390/md21030161. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36976210 Free PMC article.
-
Peromyscus spp. Deer Mice as Rodent Model of Acute Leptospirosis.Emerg Infect Dis. 2025 Jul;31(7):1365-1376. doi: 10.3201/eid3107.241579. Emerg Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40562727 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential pulmonary functions in survivors of leptospirosis pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome: a prospective cohort study.Trop Med Health. 2024 Dec 19;52(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s41182-024-00665-6. Trop Med Health. 2024. PMID: 39696512 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Pulmonary Manifestations in Leptospirosis: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2025 Jul 10;17(7):e87656. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87656. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40786414 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospirosis in Malaysia: current status, insights, and future prospects.J Physiol Anthropol. 2023 Dec 12;42(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40101-023-00347-y. J Physiol Anthropol. 2023. PMID: 38087323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scoot GM, Coleman TJ. Leptospirosis. In: Cook C, Zumla AI, editors. Manson’s tropical diseases. British: Saunders Elsevier; 2009. pp. 1161–7. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200800403 - DOI
-
- Day NPJ, Edward CN. 2010 Leptospirosis. In: Cohen J, Powderly WG, Opal SM, editors. Infectious diseases. 3rd ed. Britsih: Mosby Elsevier; 2010. pp. 1241–6.
-
- Watt G. Leptospirosis. In: Ryan E, Hill D, Solomon T, Magill A. Hunter’s tropical medicine and emerging infectious diseases. 9th ed. British: Saunders Elsevier; 2013. pp 597–601.
-
- Hartskeerl RA, Wagenaar JF. Leptospirosis. In: Kasper DL, Fauci A, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson J, editors. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 19th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2015. pp. 1140–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

