Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults
- PMID: 35584623
- PMCID: PMC9133463
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100633
Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults
Abstract
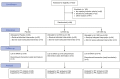
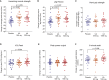
Targeting mitophagy to activate the recycling of faulty mitochondria during aging is a strategy to mitigate muscle decline. We present results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in middle-aged adults where we administer a postbiotic compound Urolithin A (Mitopure), a known mitophagy activator, at two doses for 4 months (NCT03464500). The data show significant improvements in muscle strength (∼12%) with intake of Urolithin A. We observe clinically meaningful improvements with Urolithin A on aerobic endurance (peak oxygen oxygen consumption [VO2]) and physical performance (6 min walk test) but do not notice a significant improvement on peak power output (primary endpoint). Levels of plasma acylcarnitines and C-reactive proteins are significantly lower with Urolithin A, indicating higher mitochondrial efficiency and reduced inflammation. We also examine expression of proteins linked to mitophagy and mitochondrial metabolism in skeletal muscle and find a significant increase with Urolithin A administration. This study highlights the benefit of Urolithin A to improve muscle performance.
Keywords: Mitopure; Urolithin A; aging; clinical trial; exercise performance; mitochondria; mitophagy; muscle strength.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.S., D.D., P.A.A., A.M.F., W.B.-B., and C.R. are employees, P.A. and C.R. are board members, and J.A. and P.A. are members of the Scientific Advisory Board of Amazentis SA, who is the sponsor of this clinical study.
Figures


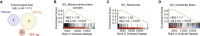

References
-
- Denison H.J., Cooper C., Sayer A.A., Aihie Sayer A., Robinson S.M. Prevention and optimal management of sarcopenia: a review of combined exercise and nutrition interventions to improve muscle outcomes in older people. Clin. Interventions Aging. 2015;10:859–869. doi: 10.2147/cia.s55842. https://www.dovepress.com/prevention-and-optimal-management-of-sarcopeni... - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goodpaster B.H., Park S.W., Harris T.B., Kritchevsky S.B., Nevitt M., Schwartz A.V., Simonsick E.M., Tylavsky F.A., Visser M., Newman A.B., for the Health ABC Study The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: the health, aging and body composition study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A. 2006;61:1059–1064. doi: 10.1093/gerona/61.10.1059. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

