The Effect of Delivery Systems on the Induction of T Helper 1 Cell Response to an ESAT6-Like Protein Rv3619c and Identification of Its Immunodominant Peptides
- PMID: 35584661
- PMCID: PMC9485963
- DOI: 10.1159/000525136
The Effect of Delivery Systems on the Induction of T Helper 1 Cell Response to an ESAT6-Like Protein Rv3619c and Identification of Its Immunodominant Peptides
Abstract
Objective: This study determined the effects of chemical adjuvants, incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA) and aluminum hydroxide (Alum), mycobacteria, and a DNA plasmid as delivery systems on the induction of protective Th1 (interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)) and nonprotective Th2 (IL-5) and Treg (IL-10) cytokine responses to Rv3619c and its peptides. Rv3619c is an immunodominant Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigen and belongs to the early-secreted antigenic target of 6 kDa-family of proteins. Delivery systems are needed to deliver such antigens in animal models and induce protective immune responses.
Methods: The rv3619c gene was amplified from the genomic DNA of M. tuberculosis and cloned into appropriate vectors for expression in Escherichia coli, Mycobacterium smegmatis, and eukaryotic cells. Spleen cells from mice immunized with rv3619c using different delivery systems were stimulated in vitro with synthetic peptides (P1 to P6) of Rv3619c, and secreted cytokines were estimated by ELISA.
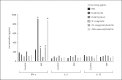
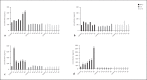
Results: The recombinant M. smegmatis and DNA plasmid induced the secretion of the protective cytokine IFN-γ in response to peptide-pool of Rv3619c and all the individual peptides, whereas rv3619c/IFA induced the secretion of IFN-γ in response to the peptide pool, and the peptides P5 and P6. However, the secretions of the nonprotective cytokines IL-5 and IL-10 were induced to none of the peptides with the delivery systems used.
Conclusion: Rv3619c is a major antigen of M. tuberculosis with multiple immunogenic epitopes; however, immune responses to individual epitopes can vary based on delivery systems used.
Keywords: Delivery systems; IFN-γ; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Peptides; Rv3619c.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brandt L, Oettinger T, Holm A, Andersen AB, Andersen P. Key epitopes on the ESAT-6 antigen recognized in mice during the recall of protective immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1996;157:3527–33. - PubMed
-
- Mustafa AS, Amoudy HA, Wiker HG, Abal AT, Ravn P, Oftung F, et al. Comparison of antigen-specific T-cell responses of tuberculosis patients using complex or single antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Scand J Immunol. 1998;48:535–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

