WEE1 inhibition enhances the antitumor immune response to PD-L1 blockade by the concomitant activation of STING and STAT1 pathways in SCLC
- PMID: 35584676
- PMCID: PMC9449677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110814
WEE1 inhibition enhances the antitumor immune response to PD-L1 blockade by the concomitant activation of STING and STAT1 pathways in SCLC
Abstract
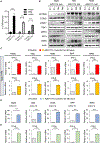
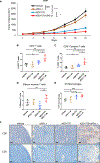
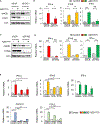
Small cell lung cancers (SCLCs) have high mutational burden but are relatively unresponsive to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). Using SCLC models, we demonstrate that inhibition of WEE1, a G2/M checkpoint regulator induced by DNA damage, activates the STING-TBK1-IRF3 pathway, which increases type I interferons (IFN-α and IFN-β) and pro-inflammatory chemokines (CXCL10 and CCL5), facilitating an immune response via CD8+ cytotoxic T cell infiltration. We further show that WEE1 inhibition concomitantly activates the STAT1 pathway, increasing IFN-γ and PD-L1 expression. Consistent with these findings, combined WEE1 inhibition (AZD1775) and PD-L1 blockade causes remarkable tumor regression, activation of type I and II interferon pathways, and infiltration of cytotoxic T cells in multiple immunocompetent SCLC genetically engineered mouse models, including an aggressive model with stabilized MYC. Our study demonstrates cell-autonomous and immune-stimulating activity of WEE1 inhibition in SCLC models. Combined inhibition of WEE1 plus PD-L1 blockade represents a promising immunotherapeutic approach in SCLC.
Keywords: CD8(+) T cells; CP: Cancer; CP: Immunology; PD-L1; SCLC; STAT1 pathway; STING pathway; WEE1 inhibition; immune checkpoint blockade; immunotherapy; interferon.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.M.R. has consulted regarding oncology drug development with AbbVie, Amgen, Ascentage, Astra Zeneca, Bicycle, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Genentech/Roche, Ipsen, Jazz, Lilly, Pfizer, PharmaMar, Syros, and Vavotek. C.M.R. serves on the scientific advisory boards of Bridge Medicines, Earli, and Harpoon Therapeutics. T.S. has received research grant from Jazz Pharmaceuticals. A.O.M. is currently employed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals; none of the work herein was funded or sponsored by Regeneron. H.M. has received a commercial research grant from Chugai Pharm and speaking honoraria from Astra Zeneca and MSD, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Antonia SJ, López-Martin JA, Bendell J, Ott PA, Taylor M, Eder JP, Jäger D, Pietanza MC, Le DT, de Braud F, et al. (2016). Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 17, 883–895. 10.1016/s1470-2045(16)30098-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Byers LA, Wang J, Nilsson MB, Fujimoto J, Saintigny P, Yordy J, Giri U, Peyton M, Fan YH, Diao L, et al. (2012). Proteomic profiling identifies dysregulated pathways in small cell lung cancer and novel therapeutic targets including PARP1. Cancer Discov. 2, 798–811. 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-12-0112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

