A noninvasive artificial neural network model to predict IgA nephropathy risk in Chinese population
- PMID: 35585099
- PMCID: PMC9117316
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11964-5
A noninvasive artificial neural network model to predict IgA nephropathy risk in Chinese population
Abstract
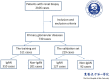
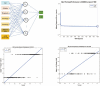
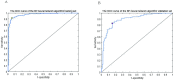
Renal biopsy is the gold standard for Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) but poses several problems. Thus, we aimed to establish a noninvasive model for predicting the risk probability of IgAN by analyzing routine and serological parameters. A total of 519 biopsy-diagnosed IgAN and 211 non-IgAN patients were recruited retrospectively. Artificial neural networks and logistic modeling were used. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and performance characteristics were determined to compare the diagnostic value between the two models. The training and validation sets did not differ significantly in terms of any variables. There were 19 significantly different parameters between the IgAN and non-IgAN groups. After multivariable logistic regression analysis, age, serum albumin, serum IgA, serum immunoglobulin G, estimated glomerular filtration rate, serum IgA/C3 ratio, and hematuria were found to be independently associated with the presence of IgAN. A backpropagation network model based on the above parameters was constructed and applied to the validation cohorts, revealing a sensitivity of 82.68% and a specificity of 84.78%. The area under the ROC curve for this model was higher than that for logistic regression model (0.881 vs. 0.839). The artificial neural network model based on routine markers can be a valuable noninvasive tool for predicting IgAN in screening practice.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A non-invasive diagnostic model of immunoglobulin A nephropathy and serological markers for evaluating disease severity.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Mar 20;132(6):647-652. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000121. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 30855344 Free PMC article.
-
High serum IgA/C3 ratio better predicts a diagnosis of IgA nephropathy among primary glomerular nephropathy patients with proteinuria ≤ 1 g/d: an observational cross-sectional study.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Apr 30;20(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1331-0. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31039758 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot and comparative study between pathological and serological levels of immunoglobulin and complement among three kinds of primary glomerulonephritis.BMC Immunol. 2018 Jun 20;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12865-018-0254-z. BMC Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29925312 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin G deposits complicated by immunoglobulin A nephropathy in the renal allograft.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Jul;21 Suppl 1:48-52. doi: 10.1111/nep.12775. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 26971743 Review.
-
A Personalized Update on IgA Nephropathy: A New Vision and New Future Challenges.Nephron. 2020;144(11):555-571. doi: 10.1159/000509997. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Nephron. 2020. PMID: 32818944 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a novel combined nomogram model integrating deep learning radiomics to diagnose IgA nephropathy clinically.Ren Fail. 2023;45(2):2271104. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2271104. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37860932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Microscopic hematuria as a risk factor for IgAN progression: considering this biomarker in selecting and monitoring patients.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Dec 4;16(Suppl 2):ii19-ii27. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad232. eCollection 2023 Dec. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38053974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning-based diagnostic prediction of IgA nephropathy: model development and validation study.Sci Rep. 2024 May 30;14(1):12426. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63339-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38816457 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding patient needs and predicting outcomes in IgA nephropathy using data analytics and artificial intelligence: a narrative review.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Dec 4;16(Suppl 2):ii55-ii61. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad206. eCollection 2023 Dec. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38053972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of personalized risk prediction models for patients with IgA nephropathy: a nationwide multicenter cohort study.J Nephrol. 2025 Jul;38(6):1573-1582. doi: 10.1007/s40620-025-02338-x. Epub 2025 Jul 11. J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40643794
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

