Response to three doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine: a retrospective study of a cohort of haemodialysis patients in France
- PMID: 35585512
- PMCID: PMC9116059
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-022-02751-5
Response to three doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine: a retrospective study of a cohort of haemodialysis patients in France
Abstract
Background: The mortality rate associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is high among haemodialyzed patients. We sought to describe the serological status of haemodialysis patients having received up to three doses of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine, and to identify factors associated with a poor humoral response.
Methods: We performed a retrospective, observational study of patients attending a dialysis centre in Antibes, France. One or two of each patient's monthly venous blood samples were assayed for anti-spike (S1) immunoglobulin G (IgG).
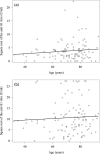
Results: We included 142 patients, of whom 124 remained COVID-19-negative throughout the study. Among these COVID-19-negative patients, the humoral immune response rate (defined as an anti-S1 IgG titre ≥1.2 U/ml) was 82.9% after two injections and 95.8% after three injections, and the median [interquartile range] titre increased significantly from 7.09 [2.21; 19.94] U/ml with two injections to 93.26 [34.25; 176.06] U/ml with three. Among patients with two injections, the mean body mass index and serum albumin levels were significantly higher in responders than in non-responders (26.5 kg/m2 vs. 23.2 kg/m2, p = 0.0392; and 41.9 g/l vs. 39.0 g/l, p = 0.0042, respectively). For the study population as a whole at the end of the study, a history of COVID-19, at least two vaccine doses, and being on the French national waiting list for kidney transplantation were the only factors independently associated with the anti-S1 IgG titre.
Conclusions: Dialysis patients vaccinated with two doses of BNT162b2 might not be sufficiently protected against SARS-CoV-2 and so should receive a third (booster) dose.
Trial registration: The present retrospective study of clinical practice was not interventional and so was not registered.
Keywords: COVID-19; Comirnaty; Haemodialysis; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jean-François Verdier, Sonia Boyer, Florence Chalmin, Ahmed Jeribi, Caroline Egasse and Philippe Auvray are employed by or under contract with the Centre de Néphrologie d’Antibes/Centre d’Hémodialyse de la Riviera. Marie France Maggi is employed by Laboratoire Bioesterel. Tarik Yalaoui is employed by B. Braun Medical SAS, Saint-Cloud, France. None of the authors have other conflicts of interest to report.
Figures



References
-
- Jager KJ, Kramer A, Chesnaye NC, Couchoud C, Sanchez-Alvarez JE, Garneata L, Collart F, Hemmelder MH, Ambuhl P, Kerschbaum J, et al. Results from the ERA-EDTA registry indicate a high mortality due to COVID-19 in dialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients across Europe. Kidney Int. 2020;98(6):1540–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

