Current challenges of high-solid anaerobic digestion and possible measures for its effective applications: a review
- PMID: 35585613
- PMCID: PMC9118646
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-022-02151-9
Current challenges of high-solid anaerobic digestion and possible measures for its effective applications: a review
Abstract
The attention that high solids anaerobic digestion process (HS-AD) has received over the years, as a waste management and energy recovery process when compared to low solids anaerobic digestion process, can be attributed to its associated benefits including water conservation and smaller digester foot print. However, high solid content of the feedstock involved in the digestion process poses a barrier to the process stability and performance if it is not well managed. In this review, various limitations to effective performance of the HS-AD process, as well as, the possible measures highlighted in various research studies were garnered to serve as a guide for effective industrial application of this technology. A proposed design concept for overcoming substrate and product inhibition thereby improving methane yield and process stability was recommended for optimum performance of the HS-AD process.
Keywords: Anaerobic digestion; Challenges; High solids; Improved measures; Inhibition; Waste management.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declared there are no competing interests.
Figures

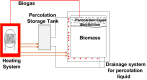

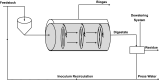


References
-
- Gallucci T, Lagioia G, Dimitrova V. Opportunities for biofuel sustainable development in Bulgaria. Int J Sustain Econ. 2010;2(3):241–257. doi: 10.1504/IJSE.2010.033393. - DOI
-
- Daniel-Gromke J, et al. Current developments in production and utilization of biogas and biomethane in Germany. Chem Ing Tech. 2017;90:17–35. doi: 10.1002/cite.201700077. - DOI
-
- Demirbas A. Potential applications of renewable energy sources, biomass combustion problems in boiler power systems and combustion related environmental issues. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2005;31(2):171–192. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2005.02.002. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
