What is the Role of the Preoperative Blood-Based Inflammation Biomarkers in the Prognosis of Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma With Radical Nephroureterectomy? A Single-Centre Retrospective Study
- PMID: 35585719
- PMCID: PMC9127859
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338221095667
What is the Role of the Preoperative Blood-Based Inflammation Biomarkers in the Prognosis of Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma With Radical Nephroureterectomy? A Single-Centre Retrospective Study
Abstract
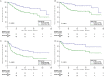
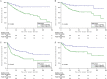
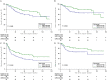
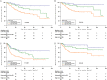
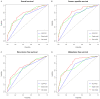
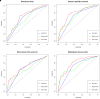
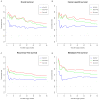
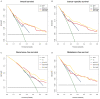
Objective: To assess the prognostic value of preoperative blood-based inflammation biomarkers, including the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio (LMR), on the survival outcomes of patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) following radical nephroureterectomy (RNU). Methods: We retrospectively studied the data of 172 patients who were diagnosed with UTUC after RNU during 2008 to 2018. We determined the cut-off value by using X-tile software. The area under the curve (AUC) and concordance index (C-index) were utilized to compare the predictive accuracy between subgroups. We also performed decision curve analysis (DCA) to evaluate the clinical net benefit of prognostic models. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards regression models were performed to evaluate the association between these inflammation biomarkers and survival outcomes. Results: The median follow-up period was 45.5 (range: 1-143; interquartile range, IQR: 27-77) months. Kaplan-Meier analyses showed that a high NLR or PLR significantly reduced overall survival (OS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), recurrence-free survival (RFS) and metastasis-free survival (MFS), and a low LMR markedly decreased RFS and MFS. The multivariate Cox proportional hazards model revealed that the NLR plus PLR was an independent predictor of worse survival (all P < .05). Additionally, the AUC and C-index of the new prognostic models were the largest for the 1- to 5-year OS, CSS, RFS, and MFS were the largest. Conclusion: Our study confirms that the combination of preoperative NLR and PLR could be an independent risk factor for UTUC patients who have undergone RNU. The addition of NLR and PLR may improve the accuracy of current prognostic models and help guide clinical strategies in the treatment of UTUC.
Keywords: inflammation biomarkers; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; radical nephroureterectomy; upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deciphering the efficiency of preoperative systemic-immune inflammation related markers in predicting oncological outcomes of upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients after radical nephroureterectomy.Investig Clin Urol. 2025 May;66(3):194-206. doi: 10.4111/icu.20250044. Investig Clin Urol. 2025. PMID: 40312899 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of preoperative lymphocyte-related systemic inflammatory biomarkers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Oct 23;18(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-02048-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33097052 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic models for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma patients after radical nephroureterectomy based on a novel systemic immune-inflammation score with machine learning.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 22;23(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11058-z. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37349696 Free PMC article.
-
Promising role of preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy.World J Urol. 2017 Jan;35(1):121-130. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1848-9. Epub 2016 May 21. World J Urol. 2017. PMID: 27209168 Free PMC article.
-
Is neutrophil-to-lymphocytes ratio a clinical relevant preoperative biomarker in upper tract urothelial carcinoma? A meta-analysis of 4385 patients.World J Urol. 2018 Jul;36(7):1019-1029. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2235-5. Epub 2018 Feb 21. World J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29468284
Cited by
-
Deciphering the efficiency of preoperative systemic-immune inflammation related markers in predicting oncological outcomes of upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients after radical nephroureterectomy.Investig Clin Urol. 2025 May;66(3):194-206. doi: 10.4111/icu.20250044. Investig Clin Urol. 2025. PMID: 40312899 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nutritional index before surgical treatment may serve as a prognostic biomarker for patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 23;9:972034. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.972034. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36211527 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for extraurothelial recurrence in upper tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy: a retrospective study based on a Chinese population.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 9;13:1164464. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1164464. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37621681 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a predictive model for postoperative metastasis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy and analysis of risk factors for different metastatic sites: a multicenter study.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Sep;57(9):2837-2851. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04455-9. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40117076
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for patients with stage II/III gastric adenocarcinoma after radical surgery.Front Surg. 2022 Oct 31;9:956256. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.956256. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36386541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seisen T, Colin P, Hupertan V, et al. Postoperative nomogram to predict cancer-specific survival after radical nephroureterectomy in patients with localised and/or locally advanced upper tract urothelial carcinoma without metastasis. BJU Int. 2014;114(5):733‐740. doi:10.1111/bju.12631 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

