Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Novel Effects in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 35585925
- PMCID: PMC9108502
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.899887
Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Novel Effects in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
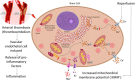
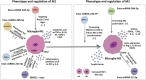
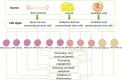
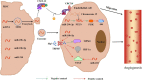
Ischemic stroke is defined as an infarction in the brain, caused by impaired cerebral blood supply, leading to local brain tissue ischemia, hypoxic necrosis, and corresponding neurological deficits. At present, revascularization strategies in patients with acute ischemic stroke include intravenous thrombolysis and mechanical endovascular treatment. However, due to the short treatment time window (<4.5 h) and method restrictions, clinical research is focused on new methods to treat ischemic stroke. Exosomes are nano-sized biovesicles produced in the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells, containing DNA, complex RNA, and protein (30-150 nm). They are released into surrounding extracellular fluid upon fusion between multivesicular bodies and the plasma membrane. Exosomes have the characteristics of low immunogenicity, good innate stability, high transmission efficiency, and the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, making them potential therapeutic modalities for the treatment of ischemic stroke. The seed sequence of miRNA secreted by exosomes is base-paired with complementary mRNA to improve the microenvironment of ischemic tissue, thereby regulating downstream signal transduction activities. With exosome research still in the theoretical and experimental stages, this review aims to shed light on the potential of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: exosomes; ischemic stroke; mesenchymal stem cells; miRNAs; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Xiong, Song, Huang, Pan, Goldbrunner, Stavrinou, Lin, Hu, Zheng and Stavrinou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson J. D., Johansson H. J., Graham C. S., Vesterlund M., Pham M. T., Bramlett C. S., et al. (2016). Comprehensive proteomic analysis of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes reveals modulation of angiogenesis via nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Stem Cells 34 601–613. 10.1002/stem.2298 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

