Cubital fossa defect- our reconstructive experience with pedicle flaps
- PMID: 35585945
- PMCID: PMC9108325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2022.04.013
Cubital fossa defect- our reconstructive experience with pedicle flaps
Abstract
Introduction: Cubital fossa wounds can be complicated by the non-availability of reliable, well-vascularized donor tissue. Closure with pliable and readily available donor tissue for cubital defect and early mobilization of the elbow joint is essential for better results. The authors did this study to see how best the results of cubital fossa defect cover can be achieved by pedicle flaps in a single stage without compromising the donor areas.
Material and method: Patients having deep elbow wounds in which vital structures were lying exposed in the cubital region were included in this study. The patients were assessed for the availability of tissue for cover, reliability of flaps, flap pliability, the functional outcome of the elbow and donor site morbidity.
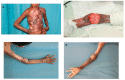
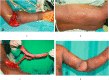
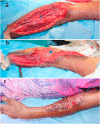
Results: A total of 17 cases of cubital region defects are presented wherein closure of the wound by means of primary closure was not possible. Out of these, eight were covered with Pedicled Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator (TDAP) flaps, five with Pedicled split Latissimus Dorsi Muscle (SLDM) flaps and four with reversed lateral arm flaps (RLA). Post-operatively all the flaps were healthy, patients attained a good range of elbow joint movements with no clinically evident morbidity of the donor site.
Conclusion: Cubital fossa defect coverage needs dedicated planning to obtain a sturdy tissue for cover. In the presence of local tissue damage or scarring, we have looked elsewhere to bring pliable and well-vascularized tissue which is reliable. The flaps we used have allowed single-stage reconstruction and early mobilization of the elbow joint with good functional recovery.
Keywords: Cubital fossa defect; Reverse lateral arm flap; Thoracodorsal artery perforator flap.
© 2022 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pedicled thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in the soft-tissue reconstruction of an acute traumatic cubital fossa defect.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022 Jul;75(7):2070-2076. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2022.02.028. Epub 2022 Feb 26. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022. PMID: 35365410
-
A clinical experience with perforator flaps in the coverage of extensive defects of the upper extremity.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004 Apr 1;113(4):1175-83. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000110332.74289.2b. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. PMID: 15083018
-
[The clinic application of thoracodorsal artery perforator flap: a report of 16 cases].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 May;29(3):178-80. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 25069342 Chinese.
-
One-stage reconstruction of composite bone and soft-tissue defects in traumatic lower extremities.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004 Nov;114(6):1457-66. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000138811.88807.65. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. PMID: 15509933 Review.
-
Focus on anatomical aspects of soft tissue coverage options in elbow reconstruction: an updating review.Surg Radiol Anat. 2018 Aug;40(8):943-954. doi: 10.1007/s00276-018-2066-5. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Surg Radiol Anat. 2018. PMID: 29992336 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

