Development of minimally invasive 13C-glucose breath test to examine different exogenous carbohydrate sources in patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia
- PMID: 35585965
- PMCID: PMC9109185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2022.100880
Development of minimally invasive 13C-glucose breath test to examine different exogenous carbohydrate sources in patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia
Abstract
Background: Glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD Ia) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase), resulting in fasting hypoglycemia. Dietary treatment with provision of uncooked cornstarch (UCCS) or a novel modified cornstarch (Glycosade®) is available to treat hypoglycemia, yet choice of carbohydrate to achieve a desirable glycemic control is debated.13C-glucose breath test (13C-GBT) can be used to examine glucose metabolism from different carbohydrate sources via 13CO2 in breath.
Objectives: Our objectives were: 1) establishing the use of a minimally invasive 13C-GBT to examine in vivo glucose metabolism in healthy adults, and 2) using 13C-GBT to measure utilization of the standard UCCS vs. Glycosade® in GSD Ia and healthy controls.
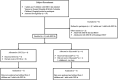
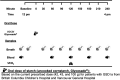
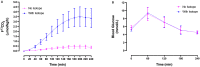
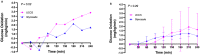
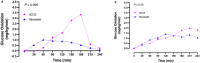
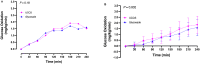
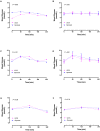
Design: Experiment 1- Ten healthy adults (6F: 4 M, 22-33y) underwent 13C-GBT protocol twice as a proof-of-principle, once with oral isotope dose (glucose 75 g + [U-13C6] d-glucose 75 mg) and once without isotope (only glucose 75 g) to test sensitivity of natural 13C-enrichment. Breath samples were collected at baseline and every 20 min for 240 min. Rate of CO2 production was measured at 120 min using indirect calorimetry. Finger-prick blood glucose was measured using a glucometer hourly to test hypoglycemia (glucose <4 mmol/L). Experiment 2- Three GSD Ia (12y, 13y, and 28y) and six healthy controls (2F: 4 M, 10-32y) underwent 13C-GBT protocol twice: with UCCS or Glycosade® (based on their current prescribed dose 42-100 g) after ~4 h fast based on our GSD Ia patients with fasting tolerance.
Results: Findings 1- Maximum 13C-enrichments occurred at 200 min without and with [U-13C6] d-glucose in all healthy adults, suggesting natural enrichment is sensitive for the 13C-GBT. Findings 2- Glycosade® utilization was lower than UCCS utilization in 12y and 13y GSD Ia, but was similar in the 28y GSD Ia.
Conclusions: 13C-GBT is a novel minimally invasive functional test to examine glucose metabolism in GSD Ia, and test new products like Glycosade®, which has the potential to improve nutritional management and individualized carbohydrate supply in GSD.
Keywords: 13C-GBT, 13C-glucose breath test; 13C-glucose; APE, atom percent excess; AUC, area under the curve; BIA, bioelectrical impedance analysis; BMI, body mass index; Breath test; CGM, continuous glucose monitor; CREU, clinical research and evaluation unit; Cmax, maximum peak enrichment in 13CO2 oxidation; F13CO2, rate of glucose oxidation; FCO2, CO2 production rate using indirect calorimetry; FFM, fat free mass; FM, fat mass; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; G6Pase, glucose-6-phosphatase; GSD I, glycogen storage disease type I; GSD Ia, glycogen storage disease type Ia; Glucose-6-phosphatase; Glycogen storage disease type Ia; Glycosade®; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; OGTT, oral glucose tolerance test; PKU, phenylketonuria; REE, resting energy expenditure; UCCS, uncooked cornstarch; Uncooked cornstarch; VCO2, rate of carbon dioxide production; tmax, time to reach maximum 13CO2 oxidation.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Nalin T., Venema K., Weinstein D.A., de Souza C.F.M., Perry I.D.S., van Wandelen M.T.R., van Rijn M., Smit G.P.A., Schwartz I.V.D., Derks T.G.J. In vitro digestion of starches in a dynamic gastrointestinal model: an innovative study to optimize dietary management of patients with hepatic glycogen storage diseases. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015;38:529–536. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9763-y. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

