Small Molecule Agents Targeting PD-1 Checkpoint Pathway for Cancer Immunotherapy: Mechanisms of Action and Other Considerations for Their Advanced Development
- PMID: 35585982
- PMCID: PMC9108255
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.752065
Small Molecule Agents Targeting PD-1 Checkpoint Pathway for Cancer Immunotherapy: Mechanisms of Action and Other Considerations for Their Advanced Development
Abstract
Pioneering success of antibodies targeting immune checkpoints such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) has changed the outlook of cancer therapy. Although these antibodies show impressive durable clinical activity, low response rates and immune-related adverse events are becoming increasingly evident in antibody-based approaches. For further strides in cancer immunotherapy, novel treatment strategies including combination therapies and alternate therapeutic modalities are highly warranted. Towards this discovery and development of small molecule, checkpoint inhibitors are actively being pursued, and the efforts have culminated in the ongoing clinical testing of orally bioavailable checkpoint inhibitors. This review focuses on the small molecule agents targeting PD-1 checkpoint pathway for cancer immunotherapy and highlights various chemotypes/scaffolds and their characterization including binding and functionality along with reported mechanism of action. The learnings from the ongoing small molecule clinical trials and crucial points to be considered for their clinical development are also discussed.
Keywords: PD-L1 inhibitors; cancer immunotherapy; mechanism of action (MOA); small molecule PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors; small molecule immunomodulators.
Copyright © 2022 Sasikumar and Ramachandra.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors are present or previous employees of Aurigene Discovery Technologies Limited. PS and MR are inventors on several patent applications related to immune checkpoint inhibitors described in this manuscript. MR is the CEO of Aurigene Discovery Technologies Limited, a company that is co-developing CA-170 for cancer therapy.
Figures



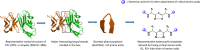

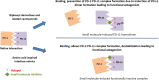
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

