Protective Effects of Tiaoganquzhi Decoction in Treating inflammatory Injury of Nonalcoholic Fatty liver Disease by Promoting CGI-58 and Inhibiting Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome
- PMID: 35586044
- PMCID: PMC9108379
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.851267
Protective Effects of Tiaoganquzhi Decoction in Treating inflammatory Injury of Nonalcoholic Fatty liver Disease by Promoting CGI-58 and Inhibiting Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome
Abstract
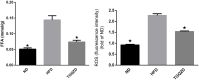
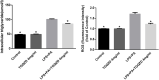
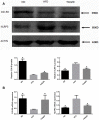
Tiaoganquzhi Decoction (TGQZD) is a traditional Chinese herbal formulation demonstrated to be a clinically effective treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), although details concerning its clinical mechanism are poor. This study aimed to explore the mechanism of TGQZD on improvement of inflammatory damage and dyslipidemia caused by NAFLD through the CGI-58/ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. In our research, the in vivo protective effects of TGQZD on HFD-induced liver injury in rats and in vitro using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)+palmitate (PA)-stimulated HepG-2 cells model. Histological changes were evaluated by hematoxylin-eosin and Oil Red O staining. Inflammatory cytokines and protein expression were analyzed by ELISA, Real time PCR and western blotting. Liver function, blood lipids, free fatty acids (FFA), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were determined by biochemical detection. Our results indicated that TGQZD exhibited anti-inflammatory activity, reduced the severity of NAFLD and ameliorated the pathological changes. Further, TGQZD improved liver function and lipid metabolism in NAFLD rats. TGQZD lowered serum aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, triglyceride, and total cholesterol levels. TGQZD suppressed the formulation of FFA and ROS. It also reduced the expression and release of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β by promoting CGI-58 expression and inhibiting the expression of FFA, TNF-α, and the NLRP3 inflammasome induced by ROS. TGQZD exhibited anti-inflammatory effects via the CGI-58, ROS and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in vivo and in vitro, respectively. Our findings demonstrated that TGQZD is a useful and effective therapeutic agent for treating NAFLD via promotion of CGI-58 to inhibit the expression of ROS-induced NLRP3 inflammasome.
Keywords: CGI-58; IL-1β; NLRP3; ROS; Tiaoganquzhi decoction; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Gao, Chen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

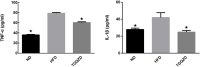


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

