New paradigm in combination therapy of siRNA with chemotherapeutic drugs for effective cancer therapy
- PMID: 35586474
- PMCID: PMC9108887
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100103
New paradigm in combination therapy of siRNA with chemotherapeutic drugs for effective cancer therapy
Abstract
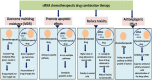
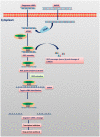
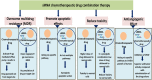
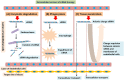
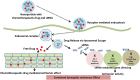
Chemotherapeutics drugs play a pivotal role in the treatment of cancer. However, many issues generate by chemotherapy drugs, including unfavorable harm to healthy cells and multidrug resistance (MDR), persist and have a negative impact on therapeutic outcomes. When compared to monotherapy, combination cancer therapy has many advantages, like improving efficacy through synergistic effects and overcoming drug resistance. Combination treatment may comprise several chemotherapeutics drugs and combinations of chemotherapeutic drugs with some other therapeutic options such as surgery or radiation. Cancer treatment that utilizes co-delivery strategies with siRNA and chemotherapeutic drugs has been shown to have highly effective antitumor effects in the treatment of many cancers. However, the highly complex mechanisms of chemotherapeutic drugs-siRNA pairs during the co-delivery process have received little attention. The ideal combination of chemotherapeutic drugs with siRNA is very crucial for producing the desirable anticancer effects that would greatly enhance therapeutic efficiency. This review puts an emphasis on the logic for choosing suitable chemotherapeutic drug-siRNA combinations, which may open the way for the co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and siRNA for treating cancer in the clinic. This review summarizes recent breakthrough in the area of diverse mechanism-based chemotherapeutic drugs-siRNA combinations in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cancer treatment; Chemotherapeutic drug; Combination therapy; Gene silencing; Multidrug resistance; RNA interference; siRNA.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships, which have, or could be perceived to have, influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reversing of multidrug resistance breast cancer by co-delivery of P-gp siRNA and doxorubicin via folic acid-modified core-shell nanomicelles.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Feb 1;138:60-9. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.11.041. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 26655793
-
Recent advances in mechanism-based chemotherapy drug-siRNA pairs in co-delivery systems for cancer: A review.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Sep 1;157:297-308. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017. PMID: 28601758 Review.
-
Nanocarrier mediated delivery of siRNA/miRNA in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for cancer therapy: current progress and advances.J Control Release. 2014 Nov 28;194:238-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 7. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25204288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery of chemotherapeutic agent and siRNA for combination cancer therapy.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017 Jan;14(1):65-73. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2016.1205583. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 27337289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in delivery of drug-nucleic acid combinations for cancer treatment.J Control Release. 2013 Dec 10;172(2):589-600. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.04.010. Epub 2013 Apr 25. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23624358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of STAT3: A promising approach to enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapy in medulloblastoma.Transl Oncol. 2024 Aug;46:102023. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102023. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38852276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional magnetic nanocapsules for dual delivery of siRNA and chemotherapy to MCF-7 cells (Breast cancer cells).Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04381-8. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40576767
-
Therapeutic delivery of siRNA for the management of breast cancer and triple-negative breast cancer.Ther Deliv. 2024;15(11):871-891. doi: 10.1080/20415990.2024.2400044. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Ther Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39320858 Review.
-
Lipopolyplex-Mediated Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and FAK siRNA to Enhance Therapeutic Efficiency of Treating Colorectal Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 10;15(2):596. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020596. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839918 Free PMC article.
-
An Orthogonally Clickable and Stimuli-Responsive Poly(β-amino ester) for the Co-delivery of Doxorubicin and BCL‑2 siRNA.ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2025 Jun 3;7(11):7013-7024. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.5c00608. eCollection 2025 Jun 13. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2025. PMID: 40535829 Free PMC article.
References
Further reading
-
- Gangopadhyay S., Nikam R.R., Gore K.R. Folate receptor-mediated small interfering RNA delivery: recent developments and future directions for RNA interference therapeutics. Feb. 2021. https://home.liebertpub.com/nat - PubMed
-
- Li A., et al. The gene transfection and endocytic uptake pathways mediated by PEGylated PEI-entrapped gold nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. Jan. 2020;13(1):2558–2567. doi: 10.1016/J.ARABJC.2018.06.009. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

