Comparative efficacy and safety of mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil for treating systemic lupus erythematosus: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 35586513
- PMCID: PMC9109492
- DOI: 10.1177/1759720X221096367
Comparative efficacy and safety of mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil for treating systemic lupus erythematosus: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Mizoribine (MZR) is an immunosuppressive agent that selectively inhibits inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; its actions are considerably similar to those of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF). This study aimed to clarify whether MZR can be a good treatment option for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to compare the efficacy and safety of MZR and MMF in patients with active SLE.
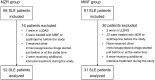
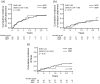
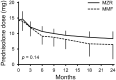
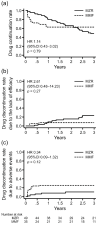
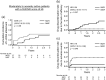
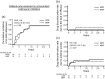
Methods: We retrospectively compared the efficacy, continuation rate, and safety of MZR (52 patients) and MMF (31 patients) after adjusting for stabilized inverse probability of treatment weighting based on propensity scores. The efficacy endpoints were as follows: cumulative incidence of lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) or remission attainment and flares and change in prednisolone dose over 2 years. Drug continuation rates were defined as the time from drug initiation to discontinuation for any cause, owing to the lack of efficacy, or owing to adverse events. The safety endpoint was the frequency of adverse events.
Results: Overall, 25 (48.1%) and 13 (25.0%) patients in the MZR group and 18 (58.1%) and 15 (48.3%) in the MMF group achieved LLDAS and remission during the follow-up period, respectively; thus, the cumulative incidence of LLDAS and remission attainment of the two groups was similar after adjustment. Prednisolone dose was steadily reduced in both the groups, and the change in prednisolone dose was nearly identical between the two groups. Drug discontinuation rate due to adverse events and the frequency of all adverse events and infections were higher in the MMF group than in the MZR group, albeit without significance after adjustment.
Conclusion: MZR is as effective as MMF in controlling SLE activity. The adverse events of MZR, whose profile differs from MMF, are comparable to or less than those of MMF. MZR may be a valuable option as an immunosuppressive agent for SLE, as well as MMF.
Keywords: continuation rate; lupus low disease activity; mizoribine; mycophenolate mofetil; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: M.Ay. and H.N. have received speaker’s fees from Asahi Kasei Pharma and Chugai Pharmaceutical. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mizoribine versus mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide for induction treatment of active lupus nephritis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(21):3718-23. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 25382325 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of mizoribine with mycophenolate mofetil for Asian renal transplantation--a meta-analysis.Clin Biochem. 2014 May;47(7-8):663-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Clin Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24463228
-
Comparison of Mizoribine and Mycophenolate Mofetil With a Tacrolimus-Based Immunosuppressive Regimen in Living-Donor Kidney Transplantation Recipients: A Retrospective Study in China.Transplant Proc. 2017 Jan-Feb;49(1):26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2016.10.018. Transplant Proc. 2017. PMID: 28104150
-
Mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil.Curr Med Chem. 1999 Jul;6(7):575-97. Curr Med Chem. 1999. PMID: 10390602 Review.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Mizoribine versus Mycophenolate Mofetil for the Treatment of Renal Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 22;2022:5717068. doi: 10.1155/2022/5717068. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35909831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fanouriakis A, Tziolos N, Bertsias G, et al.. Update in the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 2021; 80: 14–25. - PubMed
-
- Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A, et al.. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 2019; 78: 736–745. - PubMed
-
- Mak A, Cheung MW, Chiew HJ, et al.. Global trend of survival and damage of systemic lupus erythematosus: meta-analysis and meta-regression of observational studies from the1950s to 2000s. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2012; 41: 830–839. - PubMed
-
- Tselios K, Gladman DD, Sheane BJ, et al.. All-cause, cause-specific and age-specific standardised mortality ratios of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Ontario, Canada over 43 years (1971-2013). Ann Rheum Dis 2019; 78: 802–806. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

