Regulation of Plant Tannin Synthesis in Crop Species
- PMID: 35586570
- PMCID: PMC9108539
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.870976
Regulation of Plant Tannin Synthesis in Crop Species
Abstract
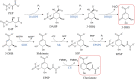
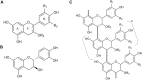
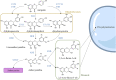
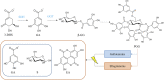
Plant tannins belong to the antioxidant compound family, which includes chemicals responsible for protecting biological structures from the harmful effects of oxidative stress. A wide range of plants and crops are rich in antioxidant compounds, offering resistance to biotic, mainly against pathogens and herbivores, and abiotic stresses, such as light and wound stresses. These compounds are also related to human health benefits, offering protective effects against cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases in addition to providing anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and anti-bacterial characteristics. Most of these compounds are structurally and biosynthetically related, being synthesized through the shikimate-phenylpropanoid pathways, offering several classes of plant antioxidants: flavonoids, anthocyanins, and tannins. Tannins are divided into two major classes: condensed tannins or proanthocyanidins and hydrolysable tannins. Hydrolysable tannin synthesis branches directly from the shikimate pathway, while condensed tannins are derived from the flavonoid pathway, one of the branches of the phenylpropanoid pathway. Both types of tannins have been proposed as important molecules for taste perception of many fruits and beverages, especially wine, besides their well-known roles in plant defense and human health. Regulation at the gene level, biosynthesis and degradation have been extensively studied in condensed tannins in crops like grapevine (Vitis vinifera), persimmon (Diospyros kaki) and several berry species due to their high tannin content and their importance in the food and beverage industry. On the other hand, much less information is available regarding hydrolysable tannins, although some key aspects of their biosynthesis and regulation have been recently discovered. Here, we review recent findings about tannin metabolism, information that could be of high importance for crop breeding programs to obtain varieties with enhanced nutritional characteristics.
Keywords: antioxidants; biosynthesis; ellagitannins (ETs); flavonoids; fruits; proanthocyanidins.
Copyright © 2022 Mora, Pott, Osorio and Vallarino.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad F., Pasha I., Saeed M., Asgher M. (2018). Biochemical Profiling of Pakistani Sorghum and Millet Varieties with Special Reference to Anthocyanins and Condensed Tannins. Int. J. Food Properties 21, 1586–1597. 10.1080/10942912.2018.1502198 - DOI
-
- Akagi T., Ikegami A., Suzuki Y., Yoshida J., Yamada M., Sato A., et al. (2009a). Expression Balances of Structural Genes in Shikimate and Flavonoid Biosynthesis Cause a Difference in Proanthocyanidin Accumulation in Persimmon (Diospyros Kaki Thunb.) Fruit. Planta 230, 899–915. 10.1007/s00425-009-0991-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

