Clinical Evidence and Potential Mechanisms of Complementary Treatment of Ling Gui Zhu Gan Formula for the Management of Serum Lipids and Obesity
- PMID: 35586687
- PMCID: PMC9110158
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7714034
Clinical Evidence and Potential Mechanisms of Complementary Treatment of Ling Gui Zhu Gan Formula for the Management of Serum Lipids and Obesity
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the clinical effects of Ling Gui Zhu Gan formula (LGZG), a famous TCM formula, for the management of serum lipids and obesity and preliminarily elucidates the bioactive components and the potential mechanism.
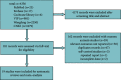
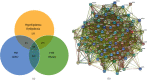
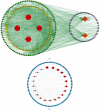
Methods: Cluster analysis was adopted to investigate the TCM herbs and their frequency of occurrence for treating hyperlipidemia and obesity in an academic experience database of Chinese famous TCM doctors (http://www.gjmlzy.com:83). Then, relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) about LGZG supplementation in improving lipid levels and obesity were retrieved and analyzed. Lastly, the integration of network pharmacology, as well as greedy algorithms, which are theoretically well founded for the set cover in computer science, was exploited to identify the bioactive components of LGZG and to reveal potential mechanisms for attenuation or reversal of hyperlipidemia and obesity.
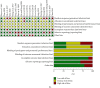
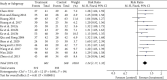
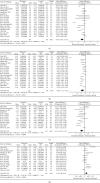
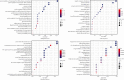
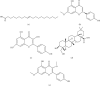
Results: Based on the cluster analysis of 104 cases in TCM academic experience database, four TCM herbs in LGZG showed high-use frequency for treating hyperlipidemia and obesity. Meta-analysis on 19 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 1716 participants indicated that LGZG supplementation significantly decreased the serum levels of total triglycerides, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, BMI, and body weight and increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, compared with clinical control groups. No serious adverse effect was detected in all studies. Twenty-one bioactive components of LGZG, mainly flavonoids (i.e., naringenin, kaempferol, and kumatakenin), saponins (i.e., hederagenin), and fatty acids (i.e., eicosenoic acid), had the potential benefits possibly by regulating multiple targets such as PTPN1, CYP19A1, and ESR2, as well as a few complex pathways including the TNF signaling pathway, PPAR signaling pathway, arachidonic acid metabolism, fat digestion, and absorption.
Conclusion: The present study has proved the clinical value of LGZG as a complementary treatment for attenuation or reversal of hyperlipidemia and obesity. More high-quality clinical and experimental studies in the future are demanded to verify its effects and the precise mechanism of action.
Copyright © 2022 Jiashuai Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The traditional Chinese formulae Ling-gui-zhu-gan decoction alleviated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibiting PPP1R3C mediated molecules.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jan 7;19(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2424-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 30616587 Free PMC article.
-
Ling-gui-zhu-gan decoction alleviates hepatic steatosis through SOCS2 modification by N6-methyladenosine.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jul;127:109976. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109976. Epub 2020 May 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32559839
-
Ling-gui-zhu-gan promotes adipocytes browning via targeting the miR-27b/PRDM16 pathway in 3T3-L1 cells.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 14;15:1386794. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1386794. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39206264 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Herbal Combinations and Pharmacological Mechanisms of Clinical Prescriptions for Coronary Heart Disease Using Data Mining and Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 23;2021:9234984. doi: 10.1155/2021/9234984. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34725557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guggul for hyperlipidemia: a review by the Natural Standard Research Collaboration.Complement Ther Med. 2005 Dec;13(4):279-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2005.08.003. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Complement Ther Med. 2005. PMID: 16338199 Review.
Cited by
-
Transdermal administration of herbal essential oil alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity by regulating metabolism and gut microbiota.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1565030. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1565030. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40176906 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating network pharmacology and animal experimental validation to investigate the action mechanism of oleanolic acid in obesity.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 21;22(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04840-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38246999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ermakova Vb H., Semenenko N. Comparative benefits of statins in coronary heart disease. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results . 2021;12(1):p. 8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

