Diaphragm Dysfunction and Rehabilitation Strategy in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 35586711
- PMCID: PMC9108326
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.872277
Diaphragm Dysfunction and Rehabilitation Strategy in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
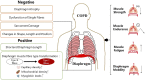
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) affects the whole body and causes many extrapulmonary adverse effects, amongst which diaphragm dysfunction is one of the prominent manifestations. Diaphragm dysfunction in patients with COPD is manifested as structural changes, such as diaphragm atrophy, single-fibre dysfunction, sarcomere injury and fibre type transformation, and functional changes such as muscle strength decline, endurance change, diaphragm fatigue, decreased diaphragm mobility, etc. Diaphragm dysfunction directly affects the respiratory efficiency of patients and is one of the important pathological mechanisms leading to progressive exacerbation of COPD and respiratory failure, which is closely related to disease mortality. At present, the possible mechanisms of diaphragm dysfunction in patients with COPD include systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, hyperinflation, chronic hypoxia and malnutrition. However, the specific mechanism of diaphragm dysfunction in COPD is still unclear, which, to some extent, increases the difficulty of treatment and rehabilitation. Therefore, on the basis of the review of changes in the structure and function of COPD diaphragm, the potential mechanism of diaphragm dysfunction in COPD was discussed, the current effective rehabilitation methods were also summarised in this paper. In order to provide direction reference and new ideas for the mechanism research and rehabilitation treatment of diaphragm dysfunction in COPD.
Keywords: COPD; diaphragm dysfunction; exercise rehabilitation; inspiratory muscle training; structural change; systemic inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Cao, Li, Wang, Liu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

