Long-Term Electrical and Mechanical Function Monitoring of a Human-on-a-Chip System
- PMID: 35586798
- PMCID: PMC9113405
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201805792
Long-Term Electrical and Mechanical Function Monitoring of a Human-on-a-Chip System
Abstract
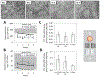
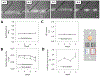
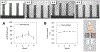
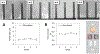
The goal of human-on-a-chip systems is to capture multi-organ complexity and predict the human response to compounds within physiologically relevant platforms. The generation and characterization of such systems is currently a focal point of research given the long-standing inadequacies of conventional techniques for predicting human outcome. Functional systems can measure and quantify key cellular mechanisms that correlate with the physiological status of a tissue, and can be used to evaluate therapeutic challenges utilizing many of the same endpoints used in animal experiments or clinical trials. Culturing multiple organ compartments in a platform creates a more physiologic environment (organ-organ communication). Here is reported a human 4-organ system composed of heart, liver, skeletal muscle and nervous system modules that maintains cellular viability and function over 28 days in serum-free conditions using a pumpless system. The integration of non-invasive electrical evaluation of neurons and cardiac cells and mechanical determination of cardiac and skeletal muscle contraction allows the monitoring of cellular function especially for chronic toxicity studies in vitro. The 28 day period is the minimum timeframe for animal studies to evaluate repeat dose toxicity. This technology could be a relevant alternative to animal testing by monitoring multi-organ function upon long term chemical exposure.
Keywords: 28-day; electrical function; mechanical function; multi-organ system; serum-free.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflict of Interest The authors confirm that competing financial interests exist but there has been no financial support for this research that could have influenced its outcome. However, JJH and MLS have a potential competing financial interest, in that a company has been formed to market services for types of cells like this in body-on-a-chip devices.
Figures



References
-
- Hutson MS, Alexander PG, Allwardt V, Aronoff DM, Bruner-Tran KL, Cliffel DE, Davidson JM, Gough A, Markov DA, Mccawley LJ, Mckenzie JR, Mclean JA, Osteen KG, Pensabene V, Samson PC, Senutovitch NK, Sherrod SD, Shotwell MS, Taylor DL, Tetz LM, Tuan RS, Vernetti LA, Wikswo JP, Appl. In Vitro Toxicol 2016, 2, 97–102.
-
- Miller PG, Shuler ML, Biotechnol. Bioeng 2016, 113, 2213–2227. - PubMed
-
- Cook D, Brown D, Alexander R, March R, Morgan P, Satterthwaite G, Pangalos MN, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2014, 13, 419–31. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
