1α, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 protects gastric mucosa epithelial cells against Helicobacter pylori-infected apoptosis through a vitamin D receptor-dependent c-Raf/MEK/ERK pathway
- PMID: 35587225
- PMCID: PMC9122358
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2058559
1α, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 protects gastric mucosa epithelial cells against Helicobacter pylori-infected apoptosis through a vitamin D receptor-dependent c-Raf/MEK/ERK pathway
Abstract
Context: Due to the resistance of Helicobacter pylori to antibiotics, it is difficult to eradicate this pathogenic bacterium from the host. The role of 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-D3) in H. pylori-infected gastric mucosa epithelial cells remains unknown.
Objective: This study investigates the protective property of 1,25-D3 against H. pylori-infected apoptosis in gastric mucosa epithelial cells and its potential molecular mechanisms.
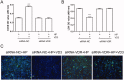
Materials and methods: GES-1 cells were infected with H. pylori SS1 strain (MOI: 100) and treated with 1,25-D3 at 100, 200, and 300 nM for 24 h. Mice were orally gavaged with 108 CFUs of H. pylori and 25 µg/kg 1,25-D3 every other day for 1 month. CCK-8, LDH assay, TUNEL assay and western blot were used to determine the effect of 1,25-D3 on H. pylori-induced apoptosis.
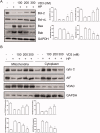
Results: H. pylori infection decreased cell viability to 59.2%, while 100-300 nM 1,25-D3 increased cell viability to 62.2%, 78.4% and 87.1%, respectively. Compared with positive control (4.53-fold), 1,25-D3 reduced caspase-3 activity to 4.49-, 2.88- and 1.49-fold, reduced caspase-6 activity to 2.36-, 1.88- and 1.50-fold, reduced caspase-9 activity to 4.55-, 2.91- and 2.01-fold. 1,25-D3 alters Bcl-2 family, caspase protein expression and c-Raf/MEK/ERK phosphorylation levels in vivo and in vitro. Suppression of 1,25-D3 in apoptosis was reliant on binding to vitamin D receptor. The pharmacological inhibition of c-Raf/MEK/ERK phosphorylation blocked the anti-apoptotic effect of 1,25-D3.
Discussion and conclusion: 1,25-D3 protected gastric mucosa epithelial cells against H. pylori-infected apoptosis through a VDR-dependent c-Raf/MEK/ERK pathway.
Keywords: Bcl-2 family; Cell proliferation; caspase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Vitamin D3 activates the autolysosomal degradation function against Helicobacter pylori through the PDIA3 receptor in gastric epithelial cells.Autophagy. 2019 Apr;15(4):707-725. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1557835. Epub 2019 Jan 6. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30612517 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori induces increased expression of the vitamin d receptor in immune responses.Helicobacter. 2014 Feb;19(1):37-47. doi: 10.1111/hel.12102. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Helicobacter. 2014. PMID: 24188043
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor activation protects gastric epithelial cells from Helicobacter pylori-induced apoptosis.Gastroenterology. 2009 Apr;136(4):1297-1307, e1-3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.059. Epub 2009 Jan 1. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19250983 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of changes in epithelial cell turnover during Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric carcinogenesis.Gut. 1998 Jul;43 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S27-32. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.2008.s27. Gut. 1998. PMID: 9764036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis by Helicobacter pylori in immune pathogenesis of gastric mucosal damage.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017 Feb;50(1):4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 29. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017. PMID: 26947589 Review.
Cited by
-
Promising anti-Helicobacter pylori and anti-inflammatory metabolites from unused parts of Phoenix dactylifera CV 'Zaghloul': in vitro and in silico study.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):657-665. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2200841. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37092359 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Vitamin D Receptor Modulating Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Gastric Cancer.J Cancer. 2023 Oct 2;14(17):3285-3294. doi: 10.7150/jca.81034. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37928423 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum vitamin D levels on Helicobacter pylori infection: a retrospective study with real-world data.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Nov 13;23(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-03037-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37957555 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D3 eradicates Helicobacter pylori by inducing VDR-CAMP signaling.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1033201. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1033201. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36569092 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Its Association with H. pylori Prevalence and Eradication: A Comprehensive Review.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 11;15(16):3549. doi: 10.3390/nu15163549. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37630738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bergogne-Bérézin E. 2000. Treatment and prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhea. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 16(4):801–526. - PubMed
-
- Burucoa C, Axon A.. 2017. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 22:e12403. - PubMed
-
- Camilo V, Sugiyama T, Touati E.. 2017. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 22:e12405. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
