Advances in research on the protective mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 35587352
- PMCID: PMC9132412
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2063342
Advances in research on the protective mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
Context: Developing effective drugs to treat myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion (MI/R) injury is imperative. Traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) have had considerable success in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Elucidating the mechanisms by which TCMs improve MI/R injury can supplement the literature on MI/R prevention and treatment.
Objective: To summarise TCMs and their main protective mechanisms against MI/R injury reported over the past 40 years.
Methods: Relevant literature published between 1980 and 2020 in Chinese and English was retrieved from the Web of Science, PubMed, SpringerLink, PubMed Central, Scopus, and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases. Search terms included 'medicinal plants', 'myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury', 'Chinese medicine prescriptions', 'mechanisms', 'prevention', 'treatment' and 'protection'. For inclusion in the analysis, medicinal plants had to be searchable in the China Medical Information Platform and Plant Database.
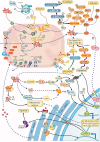
Results: We found 71 medicinal species (from 40 families) that have been used to prevent MI/R injury, of which Compositae species (8 species) and Leguminosae species (7 species) made up the majority. Most of the effects associated with these plants are described as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory. Furthermore, we summarised 18 kinds of Chinese compound prescriptions, including the compound Danshen tablet and Baoxin pill, which mainly reduce oxidative stress and regulate mitochondrial energy metabolism.
Discussion and conclusions: We summarised TCMs that protect against MI/R injury and their pharmacological mechanisms. This in-depth explanation of the roles of TCMs in MI/R injury protection provides a theoretical basis for the research and development of TCM-based treatment drugs.
Keywords: Chinese compound prescriptions; Compositae; anti-inflammatory; antioxidative; flavonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bidirectional effects and mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115578. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115578. Epub 2022 Jul 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35917892 Review.
-
Research landscape and pharmacological mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicines in treating and preventing urolithiasis: Unearthing an anti-urolithic treasure trove.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Nov 15;334:118502. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118502. Epub 2024 Jun 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38950794 Review.
-
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis using Chinese medicinal plants: From pharmacology to potential molecular mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:177-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26471289 Review.
-
Mitigation of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced chronic heart failure via Shexiang Baoxin Pill-mediated regulation of the S1PR1 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jun;128:155390. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155390. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38569296
-
Mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis and the effects of traditional Chinese medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117432. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117432. Epub 2023 Nov 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37992880 Review.
Cited by
-
Shenxiong glucose injection inhibits oxidative stress and apoptosis to ameliorate isoproterenol-induced myocardial ischemia in rats and improve the function of HUVECs exposed to CoCl2.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 5;13:931811. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.931811. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36686658 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine as a protective strategy against chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: An overview of the literature.J Tradit Complement Med. 2024 Jun 22;15(2):107-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.06.010. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Tradit Complement Med. 2024. PMID: 40060147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tanshinone IIA reduces tubulointerstitial fibrosis by suppressing GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis.Pharm Biol. 2025 Dec;63(1):364-373. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2498166. Epub 2025 May 7. Pharm Biol. 2025. PMID: 40331369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS.. 1999. Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol. 58(11):931–1693. - PubMed
-
- Bhandary B, Piao CS, Kim DS, Lee GH, Chae SW, Kim HR, Chae HJ.. 2012. The protective effect of rutin against ischemia/reperfusion-associated hemodynamic alteration through antioxidant activity. Arch Pharm Res. 35(6):1091–1097. - PubMed
-
- Bradic J, Zivkovic V, Srejovic I, Jakovljevic V, Petkovic A, Turnic TN, Jeremic J, Jeremic N, Mitrovic S, Sobot T, et al. . 2019. Protective effects of Galium verum L. extract against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:4235405. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
