Linear viscoelastic properties of the vertex model for epithelial tissues
- PMID: 35587514
- PMCID: PMC9159552
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010135
Linear viscoelastic properties of the vertex model for epithelial tissues
Abstract
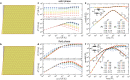
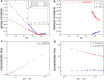
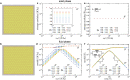
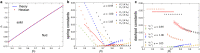
Epithelial tissues act as barriers and, therefore, must repair themselves, respond to environmental changes and grow without compromising their integrity. Consequently, they exhibit complex viscoelastic rheological behavior where constituent cells actively tune their mechanical properties to change the overall response of the tissue, e.g., from solid-like to fluid-like. Mesoscopic mechanical properties of epithelia are commonly modeled with the vertex model. While previous studies have predominantly focused on the rheological properties of the vertex model at long time scales, we systematically studied the full dynamic range by applying small oscillatory shear and bulk deformations in both solid-like and fluid-like phases for regular hexagonal and disordered cell configurations. We found that the shear and bulk responses in the fluid and solid phases can be described by standard spring-dashpot viscoelastic models. Furthermore, the solid-fluid transition can be tuned by applying pre-deformation to the system. Our study provides insights into the mechanisms by which epithelia can regulate their rich rheological behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Viscoelastic properties of suspended cells measured with shear flow deformation cytometry.Elife. 2022 Sep 2;11:e78823. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78823. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36053000 Free PMC article.
-
Ex vivo bovine liver nonlinear viscoelastic properties: MR elastography and rheological measurements.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023 Feb;138:105638. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2022.105638. Epub 2022 Dec 28. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023. PMID: 36623403
-
Linear and nonlinear rheological behavior of fat crystal networks.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018;58(14):2398-2415. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1325835. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28471278 Review.
-
Viscoelastic properties of a mixed culture biofilm from rheometer creep analysis.Biofouling. 2003 Oct;19(5):279-85. doi: 10.1080/0892701031000152470. Biofouling. 2003. PMID: 14650082
-
Viscoelastic mechanics of living cells.Phys Life Rev. 2025 Jul;53:91-116. doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2025.02.004. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Phys Life Rev. 2025. PMID: 40043484 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrodynamics and multiscale order in confluent epithelia.Elife. 2024 Jan 8;13:e86400. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86400. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38189410 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Level Modelling of Homeostasis in Confined Epithelial Monolayers.J Elast. 2025;157(2):29. doi: 10.1007/s10659-025-10120-0. Epub 2025 Feb 24. J Elast. 2025. PMID: 40013236 Free PMC article.
-
Vertex models capturing subcellular scales in epithelial tissues.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 May 21;21(5):e1012993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012993. eCollection 2025 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40397938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discontinuous Shear Thickening in Biological Tissue Rheology.Phys Rev X. 2024 Jan-Mar;14(1):011027. doi: 10.1103/physrevx.14.011027. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Phys Rev X. 2024. PMID: 38994232 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced extracellular matrix remodeling due to embedded spheroid fluidization.New J Phys. 2025 Jul 1;27(7):073301. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/ade81e. Epub 2025 Jul 10. New J Phys. 2025. PMID: 40656459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ross MH, Pawlina W. Histology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

