Effect of ArtemiC in patients with COVID-19: A Phase II prospective study
- PMID: 35587574
- PMCID: PMC9170814
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17337
Effect of ArtemiC in patients with COVID-19: A Phase II prospective study
Abstract
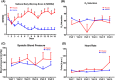
Despite intensive efforts, there is no effective remedy for COVID-19. Moreover, vaccination efficacy declines over time and may be compromised against new SARS-CoV-2 lineages. Therefore, there remains an unmet need for simple, accessible, low-cost and effective pharmacological anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. ArtemiC is a medical product comprising artemisinin, curcumin, frankincense and vitamin C, all of which possess anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. The present Phase II placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multi-centred, prospective study evaluated the efficacy and safety of ArtemiC in patients with COVID-19. The study included 50 hospitalized symptomatic COVID-19 patients randomized (2:1) to receive ArtemiC or placebo oral spray, twice daily on Days 1 and 2, beside standard care. A physical examination was performed, and vital signs and blood tests were monitored daily until hospital discharge (or Day 15). A PCR assessment of SARS-CoV-2 carriage was performed at screening and on last visit. ArtemiC improved NEWS2 in 91% of patients and shortened durations of abnormal SpO2 levels, oxygen supplementation and fever. No treatment-related adverse events were reported. These findings suggest that ArtemiC curbed deterioration, possibly by limiting cytokine storm of COVID-19, thus bearing great promise for COVID-19 patients, particularly those with comorbidities.
Keywords: ArtemiC; COVID-19; Vitamin C; artemisinin; curcumin.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

